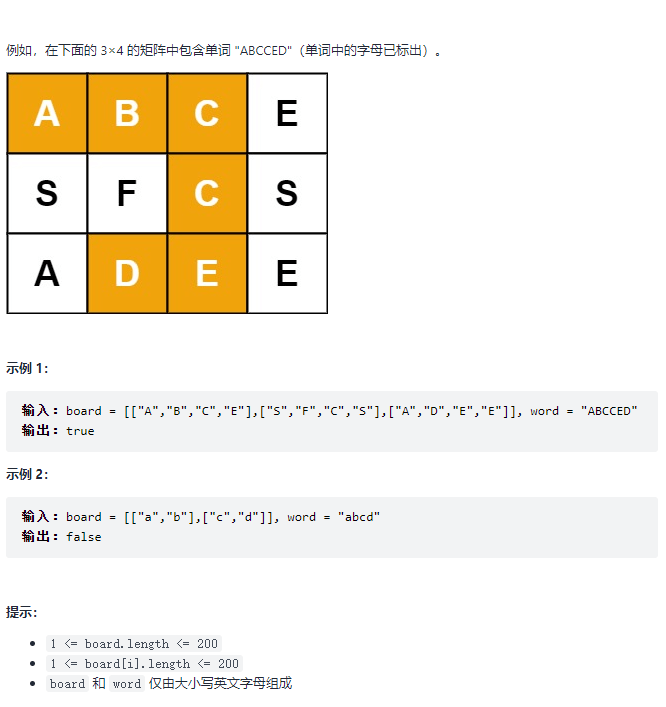
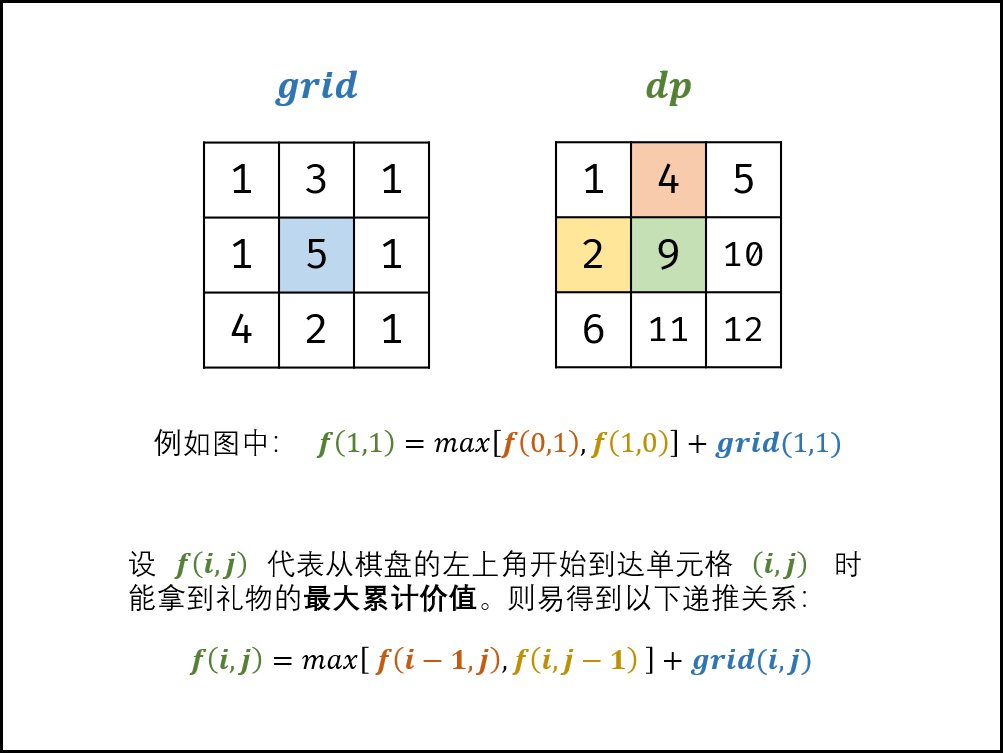LeetCode 剑指 Offer 刷题笔记
✔️Day 1 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第一天》
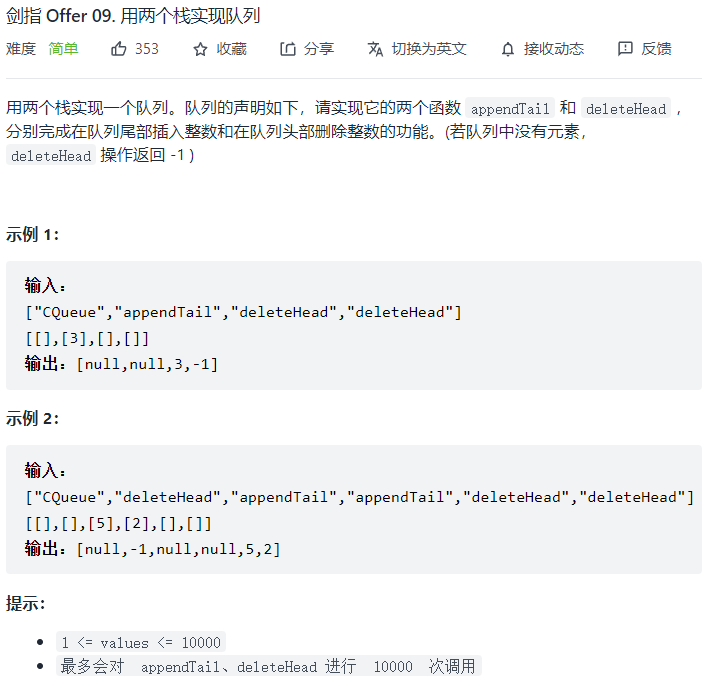
09.用两个栈实现队列 题目:剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
解题思路
用两个栈来管理进队出队,stack1 负责进队,stack2 负责出队;
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class CQueue {private Stack<Integer> stack1;private Stack<Integer> stack2;public CQueue () {new Stack ();new Stack ();public void appendTail (int value) {public int deleteHead () {if (stack2.isEmpty()) {while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {if (stack2.isEmpty()) {return -1 ;return stack2.pop();
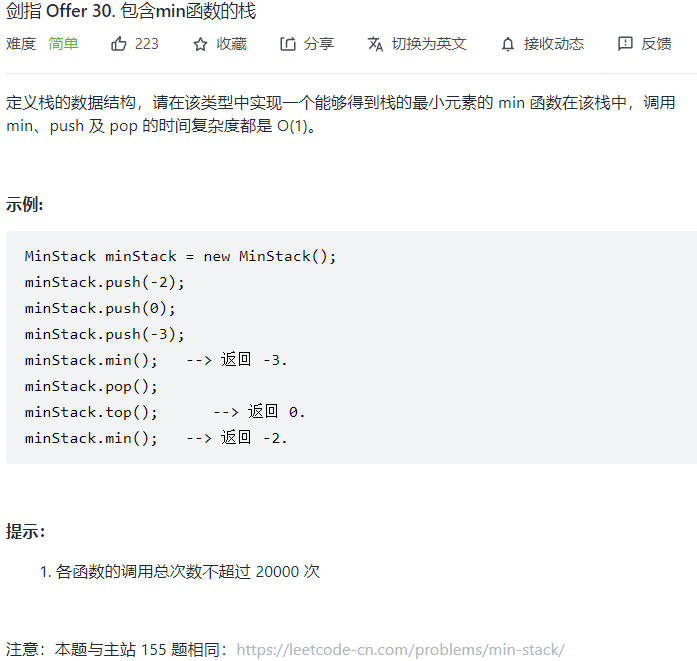
30.包含 main 函数的栈 题目:剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
题解代码
看了题解发现了好多种思路,大体上有两种:
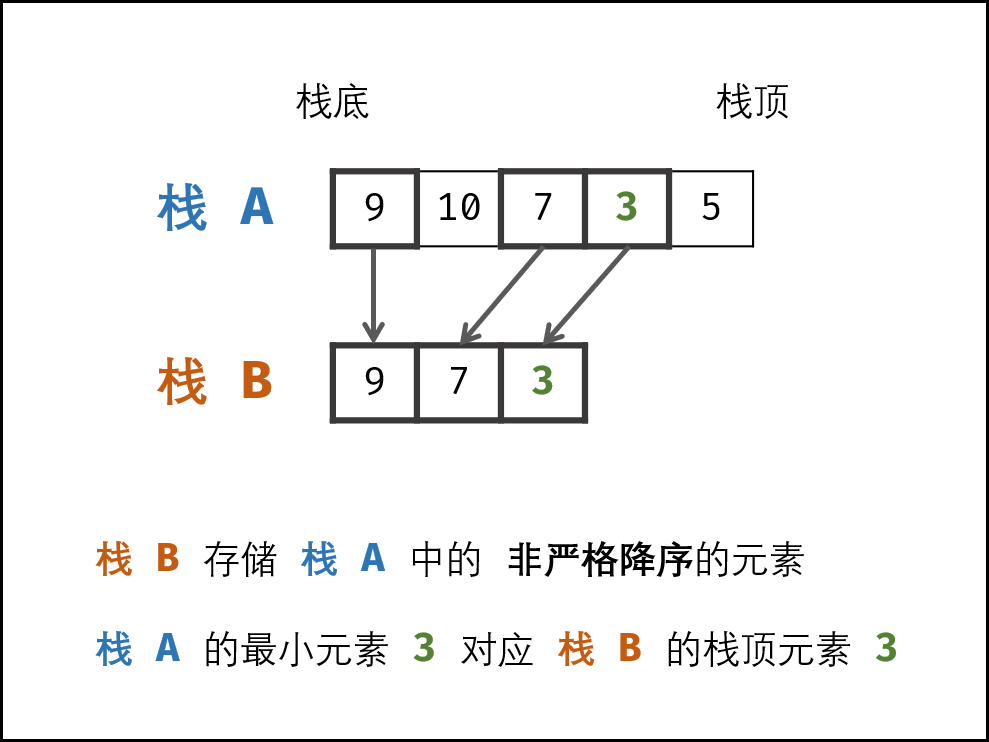
空间换时间,每次压栈都会将栈顶元素与当前元素比较,并将这个值记录下来,等于说栈内每个元素都是一个数p组, stack.push([压栈元素,当前栈最小值]) 降序辅助栈 ,内存消耗更少了些。
第二种思路巧妙,利用差值法将存入元素进行变换,出栈时再进行还原;
存入的是:非负数 -> 栈中的值 + 当前最小值 (还原)存入的是:负数 -> 当前最小值 - 栈顶 (还原), 且更新最小值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class MinStack {long m;public MinStack () {new Stack <Long>();public void push (int x) {if (A.isEmpty()) {long ) 0 );long ) x;else {long ) x - m);long ) x, m);public void pop () {long p = A.pop();if (p < 0 ) {public int top () {long p = A.peek();if (p < 0 ) {return (int ) m;else {return (int ) (m + p);public int min () {return (int ) m;
二刷代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class MinStack {private Stack<Integer> stack1;private Stack<Integer> stack2;public MinStack () {new Stack ();new Stack ();public void push (int x) {if (stack2.isEmpty()) {return ;if (x <= stack2.peek()) {public void pop () {if (stack2.peek().equals(stack1.pop())) {public int top () {return stack1.peek();public int min () {return stack2.peek();
✔️Day 2 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第二天》
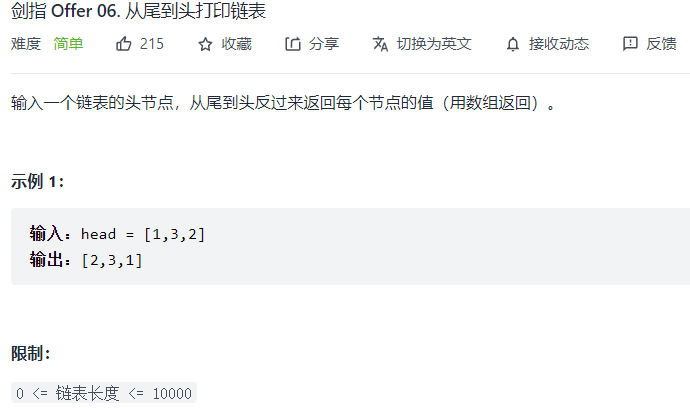
06. 从尾到头打印链表 题目:剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
解题思路(两种)
由于链表的不确定性(长度不确定),我使用了栈去存储链表的每个结点的值最后一一出栈,存入数组中得到答案。 二次遍历链表,第一次遍历获取链表的长度 len ,第二次遍历将链表的值反向压入数组中 [len - 1 - i] 。 两种方案思路基本一致,方案二时间上应该是与第一种方案无异,在空间上节省了一个存储栈(辅助栈)的空间。
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {private final Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>();public int [] reversePrint(ListNode head) {while (head != null ) {int [] retVal = new int [stack.size()];int count = 0 ;while (!stack.isEmpty()) {return retVal;
二次解答(递归)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution {private int [] retVal;private int i = 0 ;private int j = 0 ;public int [] reversePrint(ListNode head) {return retVal;public void solve (ListNode head) {if (head == null ) { new int [i]; return ;
24. 反转链表 题目:剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
解题思路
和剑指 Offer 6 一样使用辅助栈即可。
看了题解,使用双指针实现;
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {private final Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack <>();public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) {if (null == head) { return head;while (head != null ) {ListNode revHead = stack.pop();ListNode node = revHead; while (!stack.isEmpty()) {null ;return revHead;
二刷(双指针)
private final Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack <>();public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) {if (null == head) { return null ;ListNode revHead = null ,tmp = null ;while (head != null ) {return revHead;
画图演示清楚即可,附上 leetcode 动态演示图;
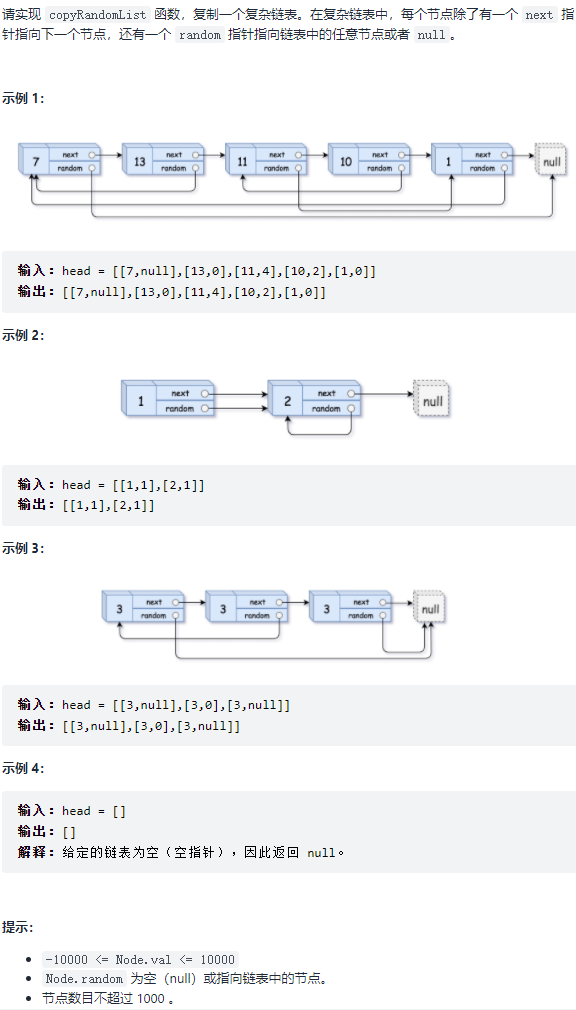
35. 复杂链表的复制 题目:剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
思路一 利用哈希表的查询特点,考虑构建 原链表节点 和 新链表对应节点 的键值对映射关系,再遍历构建新链表各节点的 next 和 random 引用指向即可。
算法流程
若头节点 head 为空节点,直接返回 null; 初始化: 哈希表 dic , 节点 cur 指向头节点; 复制链表:建立新节点,并向 dic 添加键值对 (原 cur 节点, 新 cur 节点) ; cur 遍历至原链表下一节点; 构建新链表的引用指向:构建新节点的 next 和 random 引用指向; cur 遍历至原链表下一节点; 返回值: 新链表的头节点 dic[cur] ; 复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N): 两轮遍历链表,使用 O(N) 时间。 空间复杂度 O(N) : 哈希表 dic 使用线性大小的额外空间。 解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution {public Node copyRandomList (Node head) {if (head == null ) return null ;Node cur = head;new HashMap <>();while (cur != null ) {new Node (cur.val));while (cur != null ) {return map.get(head);
思路二 考虑构建 原节点 1 -> 新节点 1 -> 原节点 2 -> 新节点 2 -> …… 的拼接链表,如此便可在访问原节点的 random 指向节点的同时找到新对应新节点的 random 指向节点。
算法流程
复制各节点,构建拼接链表: 构建新链表各节点的 random 指向:当访问原节点 cur 的随机指向节点 cur.random 时,对应新节点 cur.next 的随机指向节点为 cur.random.next 。 拆分原 / 新链表:设置 pre / cur 分别指向原 / 新链表头节点,遍历执行 pre.next = pre.next.next 和 cur.next = cur.next.next 将两链表拆分开。 复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N): 三轮遍历链表,使用 O(N) 时间。 空间复杂度 O(1): 节点引用变量使用常数大小的额外空间。 解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Solution2 {public Node copyRandomList (Node head) {if (head == null ) return head;Node cur = head;while (cur != null ) { Node newNode = new Node (cur.val);while (cur != null ) { if (cur.random != null ) { Node pre = head.next, res = head.next;while (pre.next != null ) { null ; return res;
✔️Day 3 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第三天》
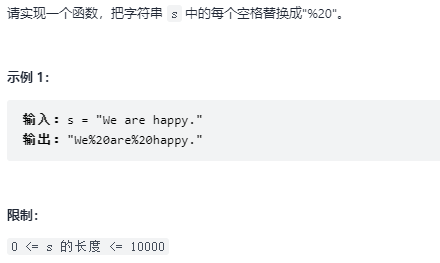
05. 替换空格 题目:剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
解题思路
使用 StringBuilder,注意字符串拼接使用 StringBuilder 要比使用 StringBuffer 更好,因为 StringBuffer 底层加了锁,是线程安全的,但是会消耗一定的性能。
简单字符串拼接使用 + 拼接性能和使用 StringBuilder 差不多,自 JDK 1.5 开始,Java 编译器就做了优化,使用 + 拼接字符串,编译器编译后实际就自动优化为使用 StringBuilder。
使用循环拼接时,每次循环都会 new 一个 StringBuilder 对象,这时使用 StringBuilder 会更好;
注意: StringBuilder 不是线程安全的!!!StringBuffer 是线程安全的!!
算法流程
遍历字符串的每个字符然后使用 StringBuilder 拼接即可;
解题代码
class Solution {public String replaceSpace (String s) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();char c;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i) {if (c == ' ' ) {"%20" );else {return builder.toString();
58 - II. 左旋转字符串 题目:剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
由于 Java 在循环中字符串拼接都是新 new 了一个对象,所以直接使用 String 内存空间消耗较大,采用 StringBuilder 对象拼接字符串;
解题代码
class Solution {public String reverseLeftWords (String s, int n) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();for (int i = n; i < s.length(); ++i) {for (int i = 0 ; i < n ;++i) {return builder.toString();
解题代码-优化?(代码简洁了,但是似乎耗时更多了)
class Solution {public String reverseLeftWords (String s, int n) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();for (int i = n; i < s.length() + n; ++i) {return builder.toString();
✔️Day 4 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第四天》
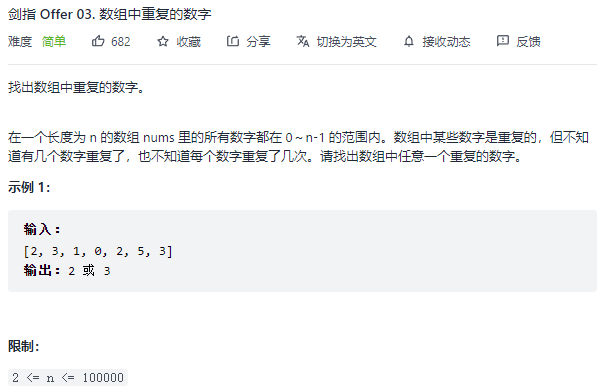
03. 数组中重复的数字 题目:剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
解题思路
构建一个计数数组 count,刚开始通过 nums 数组中的值作为 计数数组 count 的索引去进行计数,但是突然发现 n 的值有点大,最坏情况下需要开十万的数组(2 <= n <= 100000),太消耗内存空间了!
解题代码
class Solution {public int findRepeatNumber (int [] nums) {int [] count = new int [nums.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < count.length; ++i) {if (count[nums[i]] != 0 ) {return nums[i];return -1 ;
题解解法 算法流程
遍历数组 numsnums ,设索引初始值为 i = 0:若 nums[i] = i: 说明此数字已在对应索引位置,无需交换,因此跳过; 若 nums[nums[i]] = nums[i]: 代表索引 nums[i] 处和索引 ii 处的元素值都为 nums[i],即找到一组重复值,返回此值 nums[i]; 否则: 交换索引为 i 和 nums[i] 的元素值,将此数字交换至对应索引位置。 若遍历完毕尚未返回,则返回 −1 。 复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N) : 遍历数组使用 O(N) ,每轮遍历的判断和交换操作使用 O(1) 。 空间复杂度 O(1) : 使用常数复杂度的额外空间。 题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public int findRepeatNumber (int [] nums) {int i = 0 ;while (i < nums.length) {if (nums[i] == i) {continue ;if (nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]) return nums[i];int tmp = nums[i];return -1 ;
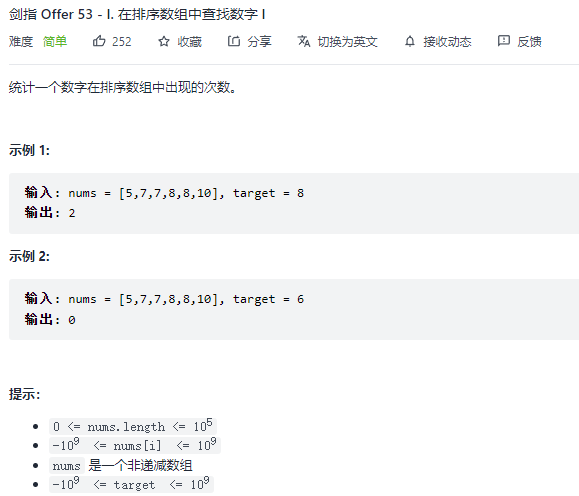
53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I 题目:剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class Solution {public static void main (String[] args) {new int []{2 ,2 }),2 ));public static int search (int [] nums, int target) {if (nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ;int begin = 0 , end = nums.length - 1 ;while (begin <= end) {int mid = begin + (end - begin) / 2 ;if (nums[mid] == target) {int count = 1 ;for (int i = mid - 1 ; i >= begin; --i) {if (mid == 0 || nums[i] != target) {break ;for (int i = mid + 1 ; i <= end; ++i) {if (i >= nums.length || nums[i] != target) {break ;return count;else if (nums[mid] < target){1 ;else {1 ;return 0 ;public int binary_search (int [] nums, int start, int end, int target) {if (start > end) {return -1 ;int mid = start + (end - start) / 2 ;if (target == nums[mid]) {return mid;if (target < nums[mid]) {return binary_search(nums, start, mid - 1 , target);return binary_search(nums, mid, end, target);
53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字 题目:剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
解题思路
高斯求和公式,做差即可,时间复杂度 O(N)
public class Solution {public int missingNumber (int [] nums) {int len = nums.length, sum = 0 ;for (int num : nums) {return (len + 1 ) * (len) / 2 - sum;
使用 异或操作,相同元素 ^ = 0(1 ^ 1 = 0 ),无本质区别,时间复杂度都是 O(N)
class Solution {public static int missingNumber (int [] nums) {for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if ((nums[i] ^ i) != 0 ) { return i;return nums.length;
题解思路
使用二分法,可以将复杂度降低至 log(N),后补!
✔️Day 5 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第五天》
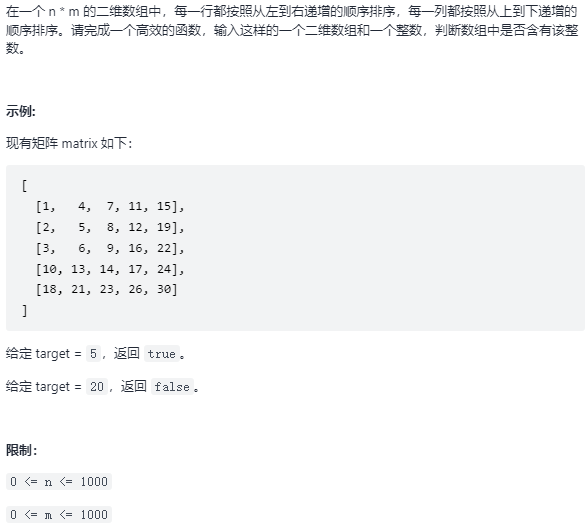
04. 二维数组中的查找 题目:剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
解题思路
从右上角开始遍历,右上角的元素具有以下性质:
它是该行最大的元素 它是该列最小的元素 通过带查找元素 target 与 这个元素比较可以主键缩小列与行;
时间复杂度 O(N M)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public boolean findNumberIn2DArray (int [][] matrix, int target) {if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 ) {return false ;int row = 0 , col = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ;while (row < matrix.length && col >= 0 ) {if (matrix[row][col] > target) {else if (matrix[row][col] < target){else {return true ;return false ;
11. 旋转数组的最小数字 题目:剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
解题思路
参数数组 numbers 的构成是 A + B,A、B分别是升序数组,且有 Max(B) <= Min(A);可以从数组末端遍历数组,找到比左端元素小的那个元素即为 B 的第一个元素,也就是最小元素;
解题代码
class Solution {public int minArray (int [] numbers) {for (int i = numbers.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; --i) {if (numbers[i] < numbers[i - 1 ]) {return numbers[i];return numbers[0 ];
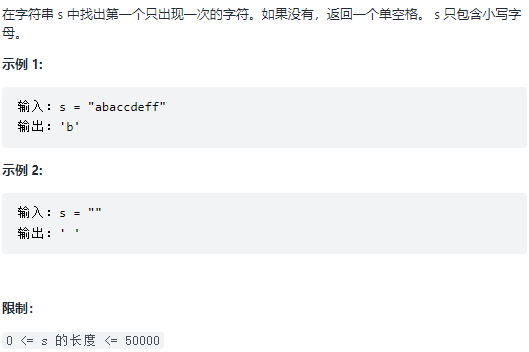
50. 第一个只出现一次的字符 题目:剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
解题思路
刚开始构建了 计数数组cout,但是后来发现与题目不太一样,技术数组只能统计个数,不能满足题干中 第一个 这个条件,后来考虑使用 Hash 表,遍历两次,第一次遍历找出只出现一次的字符,第二次找出第一个只出现一次的字符
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public char firstUniqChar (String s) {if (s.equals("" )) return ' ' ;new HashMap ();char c;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i) {if (null == exist) {true );continue ;if (map.get(c)) {false );for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i) {if (map.get(c)) return c;return ' ' ;
题解 在哈希表的基础上,有序哈希表中的键值对是 按照插入顺序排序 的。基于此,可通过遍历有序哈希表,实现搜索首个 “数量为 1 的字符”。
哈希表是 去重 的,即哈希表中键值对数量字符串 s 的长度。因此,相比于方法一,方法二减少了第二轮遍历的循环次数。当字符串很长(重复字符很多)时,方法二则效率更高。
在 Java 中有有序哈希表,可以少遍历一次字符串,Map<Character, Boolean> map = new LinkedHashMap();
class Solution {public char firstUniqChar (String s) {if (s.equals("" )) return ' ' ;new LinkedHashMap <>();char [] chs = s.toCharArray();for (char ch : chs) {for (Map.Entry<Character, Boolean> d : map.entrySet()) {if (d.getValue()) return d.getKey();return ' ' ;
✔️Day 6 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第六天》
面试题32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树 题目:面试题32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
解题思路
从上至下 打印(按层打印)二叉树,又称为二叉树的 广度优先搜索 (BFS);BFS 通常借助 队列 的先入先出特性来实现; 算法流程
特例处理: 根节点为空,直接返回空数组 [];初始化: 打印结果列表 res = [],包含根节点的队列 queue = [root] ;BFS 循环: 当前队列 queue 为空时结束循环;出队: 队首出队,记为 node;打印: 将 node.val 添加至动态数组 ans 的尾部;添加子节点: 若 node 有左(右)节点,则按照先左后右的顺序将子节点添加至队列 queue;返回值: 返回打印结果列表 res 即可复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N) : N 为二叉树的节点数量,即 BFS 需循环 N 次空间复杂度 O(N) : 最差情况下,即当树为平衡二叉树时,最多有 N/2 个树节点 同时 在 queue 中,使用 O( N) 大小的额外空间解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class Solution {public int [] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) { return new int [0 ];new LinkedList <>();new ArrayList <>(); while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null ) { if (node.right != null ) { int [] res = new int [ans.size()];for (int i = 0 ; i < ans.size(); i++) {return res;
32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II 题目:剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
解题思路
这道题和 面试题32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树 基本一样,把面试题32的代码写出来之后就没了思路,正在想队列一次只能出队一个,怎么对元素分层打印涅,突然就看到了 queue.size();牛🐂!
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();if (root != null ) {new ArrayList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0 ; --i) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ) {if (node.right != null ) {return res;
32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III 题目:剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
解题思路
都是面试题32-I 的同类型题(甚至可以说是一个题,输出格式不同 0.0),这个题个人思路加个变量统计判断奇偶决定队列顺序即可,后来实现代码后发现不太行,因为这样之后队列中下次遍历的元素与上次便利的元素有关联,比如:
[1, 2, 3, 4, null, null, 5],按照上述想法得出结果是:[[1], [3, 2], [5, 4]],与预期结果 [[1], [3, 2], [4, 5]] 结果不符合;
后来转变思路,其他部分照旧,在加入 list 前做奇偶判断,选择是否逆置数组;
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();if (root != null ) {new ArrayList <>();int count = 0 ;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0 ; --i) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ) {if (node.right != null ) {if ((count & 1 ) == 1 ) {else {new ArrayList <>();for (int i = list.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) {return res;
题解 看了大佬的题解,ArrayList 提供了一些插入方法,可以直接进行尾插,我们可以在判断奇数偶数后进行头插操作;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();if (root != null ) {new ArrayList <>();int count = 0 ;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {new LinkedList <>();for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0 ; --i) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if ((count & 1 ) == 1 ) { else { if (node.left != null ) {if (node.right != null ) {return res;
✔️Day 7 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第七天》
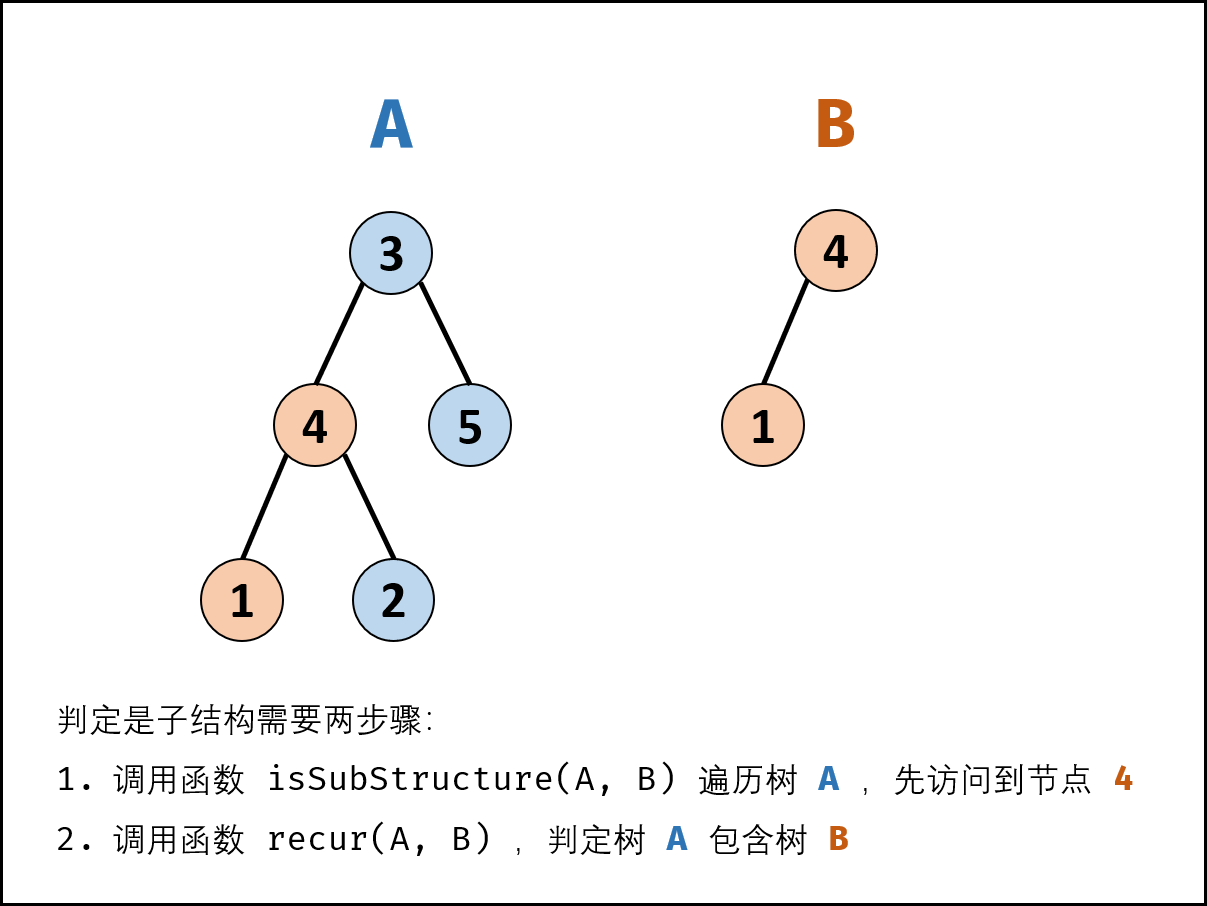
26. 树的子结构 题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-de-zi-jie-gou-lcof/
解题思路
若树 B 是树 A 的子结构,则子结构的根节点可能为树 A 的任意一个节点,因此,判断树 B 是否是树 A 的子结构,需要完成以下两部工作:
先序遍历树 A 中的每个节点 n~A~;(对应函数 isSubStructure(A, B)) 判断树 A 中 以 n~A~ 为根节点的子树 是否包含树 B ;(对应函数 isSub(A, B))
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(MN):其中 M,N 分别为 树 A 和 树 B 的节点数量; 先序遍历 树 A 占用 O(M),每次调用 isSub(A, B) 判断占用 O(N); 空间复杂度 O(M):当 树 A 和 树 B 都退化为链表时,递归调用深度最大,当 M <= N 时,遍历 树 A 与递归判断的总递归深度为 M; 当 M > N 时,最差情况遍历至 树 A 叶子节点,此时递归深度为 M; 解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public boolean isSubStructure (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {if (A == null || B == null ) {return false ;return isSub(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B);public boolean isSub (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {if (B == null ) {return true ;if (A == null || A.val != B.val) {return false ;return isSub(A.left, B.left) && isSub(A.right, B.right);
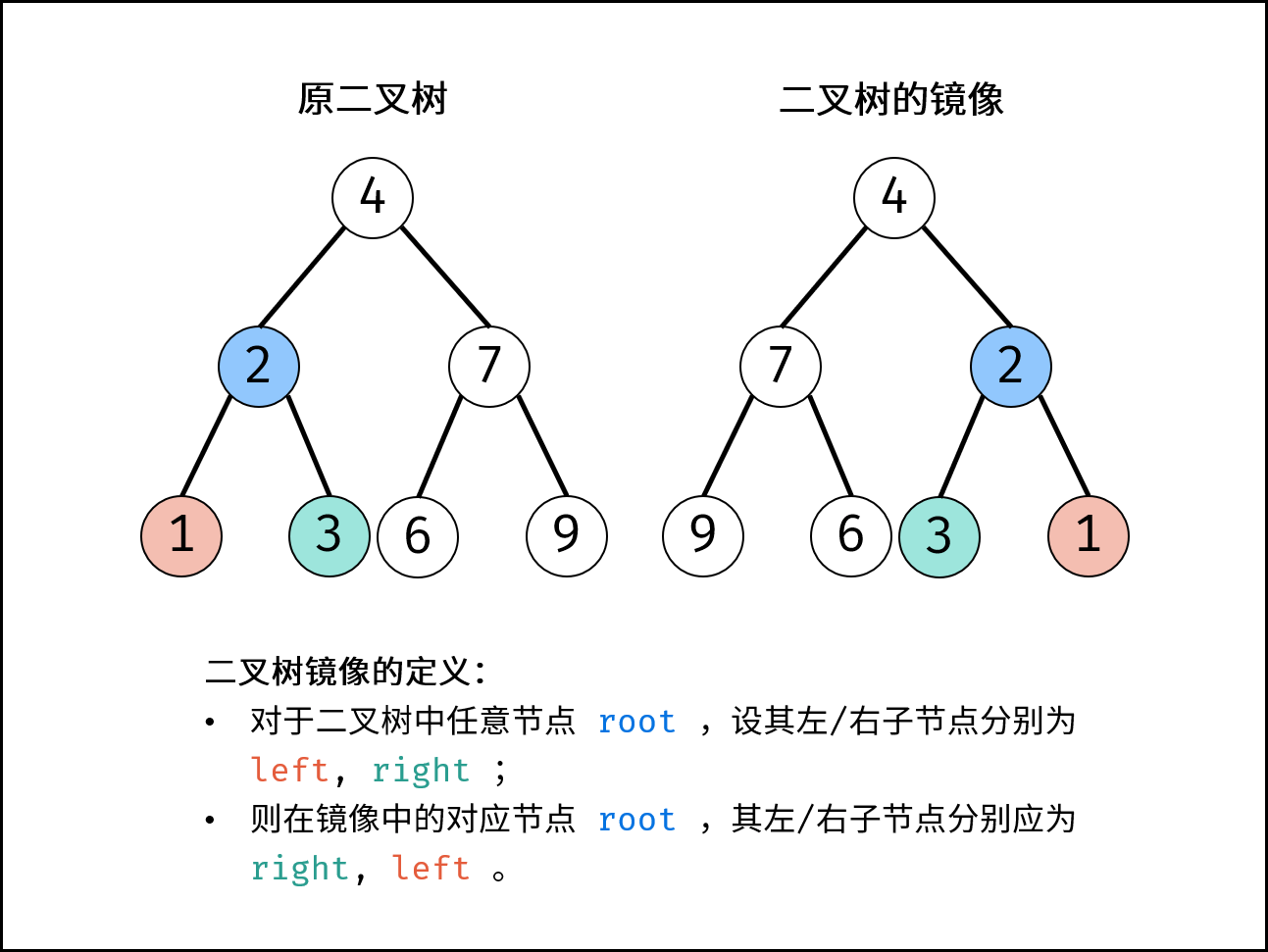
27. 二叉树的镜像 题目:剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
解题思路
递归 dfs 遍历二叉树,交换每个节点的左右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像;
Q: 为何需要暂存 root 的左子节点?
A: 在递归右子节点 root.left = mirrorTree(root.right) 执行完毕后, root.left 的值已经发生改变,此时递归左子节点 mirrorTree(root.left) 则会出问题。
class Solution {public TreeNode mirrorTree (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return root;TreeNode tmp = root.left;return root;
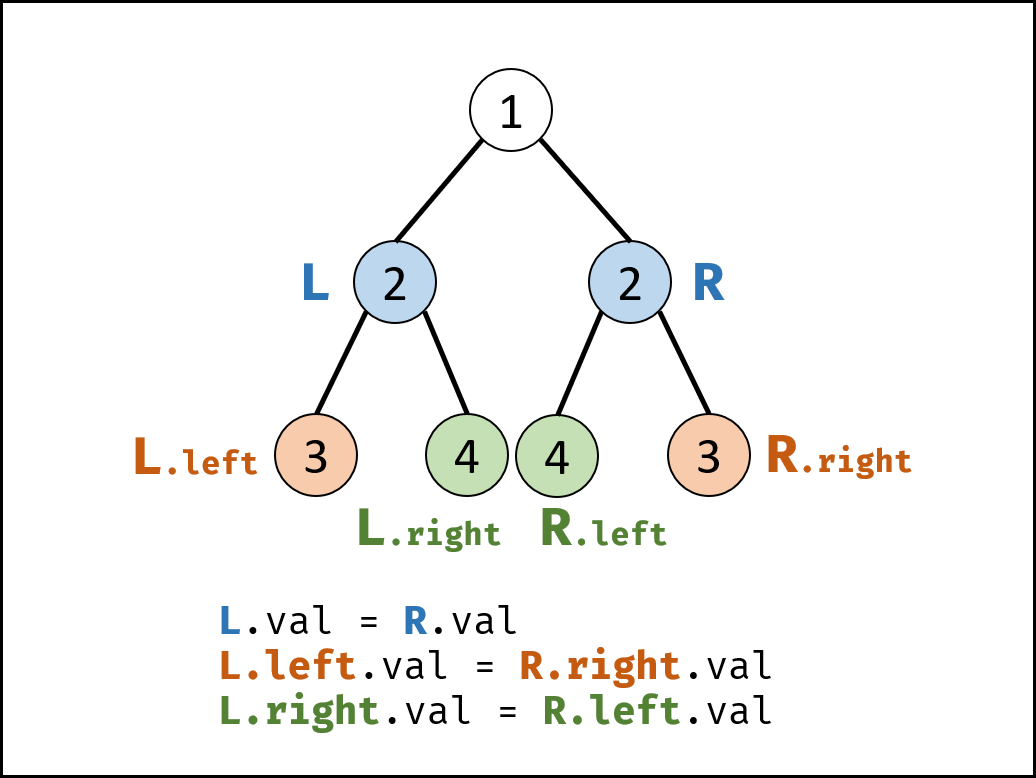
28. 对称的二叉树 题目:剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
解题思路
对于一个二叉树的任意两个对称的节点 L、R,其镜像的前提是:
L.val = R.valL.left.val = R.right.valL.right.val = R.left.val
解题代码
public class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {return root == null || isSub(root.left, root.right);public boolean isSub (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {if (A == null && B == null ) {return true ;if (A == null || B == null || A.val != B.val) {return false ;return isSub(A.left, B.right) && isSub(A.right, B.left);
✔️Day 8 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第八天》
10- I. 斐波那契数列 题目:剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
解题思路
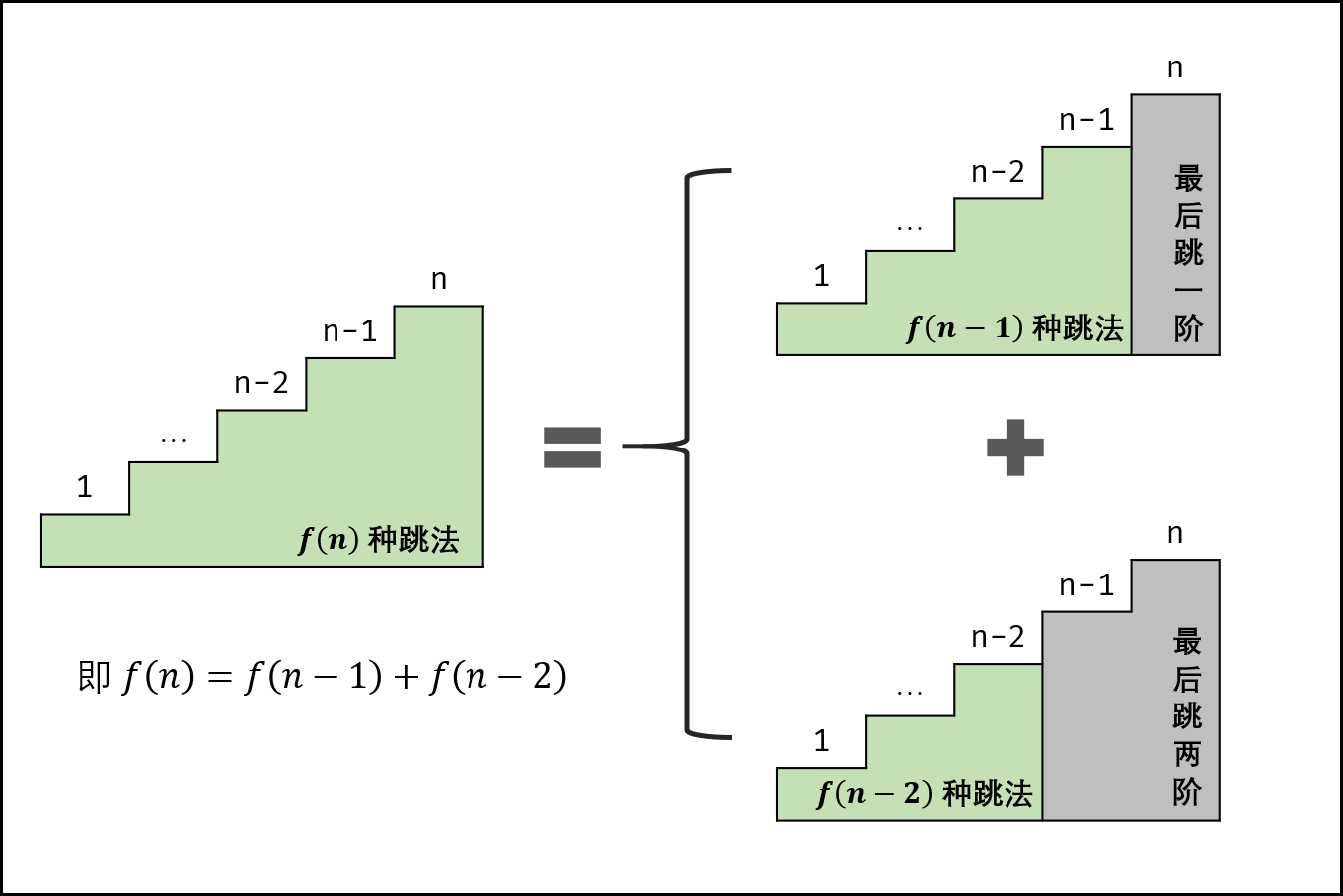
很容易推导出递归式:f(n + 1) = f(n) + f(n - 1),然后使用递归,啪的一下,很快啊,爆栈了 qaq;
使用动态规划求解:
状态定义:dp[i] 表示斐波那契数列中的第 i 个数; 递归方程:dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + dp[i - 1] 初始状态:dp[0] = 0, dp[1] = 1 返回值:dp[n] 解题代码
class Solution {private final int mod = 1000000007 ;public int fib (int n) {if (n < 2 ) {return n;int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ];0 ] = 0 ;1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; ++i) {1 ] + dp[i - 2 ]) % mod;return dp[n];
由于 dp[n] 只和 dp[n - 1] 和 dp[i - 2] 有关,所以可以节省数组空间,循环递推;
解题思路—优化
public class Solution2 {private final int mod = 1000000007 ;public int fib (int n) {if (n <= 1 ) {return n;int p = 0 , q = 1 , sum;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {return p;
10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题 题目:剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题
解题思路
基本上和斐波那契数那题一样,唯一区别就是初始状态不太一样了;
解题代码
public class Solution {private final int mod = 1000000007 ;public int numWays (int n) {if (n < 2 ) {return 1 ;int p = 1 , q = 1 , sum = 1 ;for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; ++i) {return sum;
63. 股票的最大利润 题目:剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润
解题思路
一样动态规划求解,dp[i] 代表前 i 天可以获得的最大利润;可以得知 dp[0] = 0;可以得到转移方程:dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], prices[i] - min(prices[0, i - 1]))
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {if (prices.length == 0 ) {return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [prices.length];0 ] = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; ++i) {1 ], prices[i] - min(prices, i));return dp[prices.length - 1 ];public int min (int [] arr, int size) {int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) {if (arr[i] < min) {return min;
解题代码—优化
看了题解优化了一点点,利用一个变量记录前 i 项的最小值,不必每次调用自定义 min 函数了,省了很多时间!208 ms 41.1MB -> 2 ms 41.7MB
public class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {if (prices.length == 0 ) {return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [prices.length];0 ] = 0 ;int min = prices[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; ++i) {1 ], prices[i] - min);return dp[prices.length - 1 ];
解题代码—再优化
2ms 41.7 MB -> 1 ms 41.2MB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {if (prices.length < 2 ) { return 0 ;int min = prices[0 ];int p = 0 , q;for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; ++i) {return p;
解题代码—还能优化
1ms 41.2MB -> 0ms 41.1 MB
class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE, profit = 0 ;for (int price : prices) {return profit;
✔️Day 9 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第九天》
42. 连续子数组的最大和 题目:剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和
解题思路
状态定义:设动态规划列表 dp,dp[i] 代表以元素 nums[i] 结尾的连续子数组的最大和
转移方程:若 dp[i - 1] ≤ 0,说明 dp[i - 1] 对 dp[i] 产生负贡献,即 dp[i - 1] + nums[i] ≤ nums[i] ;
初始状态:dp[0] = nums[0],即以 nums[0] 结尾的连续子数组的最大和为 nums[0]
返回值:返回 dp 列表中的最大值,代表全局最大值
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution {public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {int [] dp = new int [nums.length];0 ] = nums[0 ];int max = nums[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < dp.length; ++i) {if (dp[i - 1 ] > 0 ) {1 ];else {return max;
解题代码—优化
dp[i] 只和 dp[i - 1] 和 nums[i] 有关系,因此可以在原数组上修改用作 dp 列表;
public class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {int res = nums[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) {1 ], 0 );return res;
public class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {int max = nums[0 ];int p = nums[0 ], q;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (p > 0 ) {else {return max;
47. 礼物的最大价值 题目:剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值
解题思路
分析题目可以得到如下的递推关系:f(i, j) = max[f(i - 1, j), f(i, j - 1)]
状态定义:设动态规划矩阵 dp,dp[i][j] 表示从左上角走到单元格 (i, j) 的礼物最大累计价值
转移方程:
当 i = 0 且 j = 0 时,为起始元素; 当 i = 0 且 j ≠ 0 时,为矩阵第一行元素,只可从左边到达 当 i ≠ 0 且 j = 0 时,为矩阵第一列元素,只可从上边到达 当 i ≠ 0 且 j ≠ 0 时,可从左边或上边到达; $dp(i,j)= \begin{cases} grid(i,j) & {,i=0, j=0}\ grid(i,j) + dp(i,j-1) & {,i=0, j \ne 0}\ grid(i,j) + dp(i-1,j) & {,i \ne 0, j=0}\ grid(i,j) + \max[dp(i-1,j),dp(i,j-1)]& ,{i \ne 0, j \ne 0} \end{cases}$
初始状态:dp[0][0] = gird[0][0] ,即到达单元格 (0,0) 时能拿到礼物的最大累计价值为 grid[0][0];
返回值:dp[m - 1][n - 1],m,n 分别为矩阵的行高和列宽,即返回矩阵的右下角元素
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution {public int maxValue (int [][] grid) {int dp[][] = new int [grid.length][grid[0 ].length];for (int i = 0 ; i < grid.length; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < grid[0 ].length; ++j) {if (i == 0 && j == 0 ) { else if (i == 0 ) { 1 ] + grid[i][j];else if (j == 0 ) { 1 ][j] + grid[i][j];else { 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]);return dp[dp.length - 1 ][dp[0 ].length - 1 ];
题解代码-优化 由于 dp[i][j] 只与 dp[i-1][j] , dp[i][j-1] ,grid[i][j] 有关系,因此可以将原矩阵 grid 用作 dp 矩阵,即直接在 grid 上修改即可,可以将空间复杂度优化至 O(1)
public class Solution2 {public int maxValue (int [][] grid) {int row = grid.length, col = grid[0 ].length;for (int i = 1 ; i < col; ++i) { 0 ][i] += grid[0 ][i - 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < row; ++i) { 0 ] += grid[i - 1 ][0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < row; ++i) {for (int j = 1 ; j < col; ++j) {1 ][j], grid[i][j - 1 ]);return grid[row - 1 ][col - 1 ];
✔️Day 10 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十天》
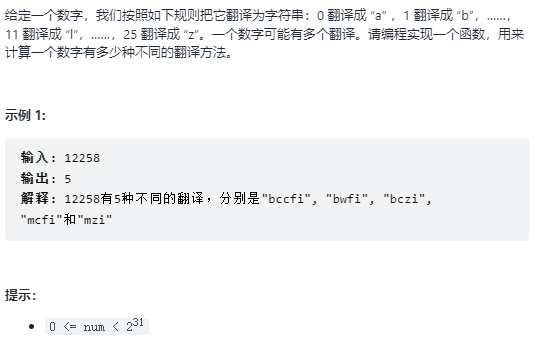
46. 把数字翻译成字符串 题目:剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
题解思路
根据题意总结出 “递推公式”,即转移方程,采用动态规划的方法解题;
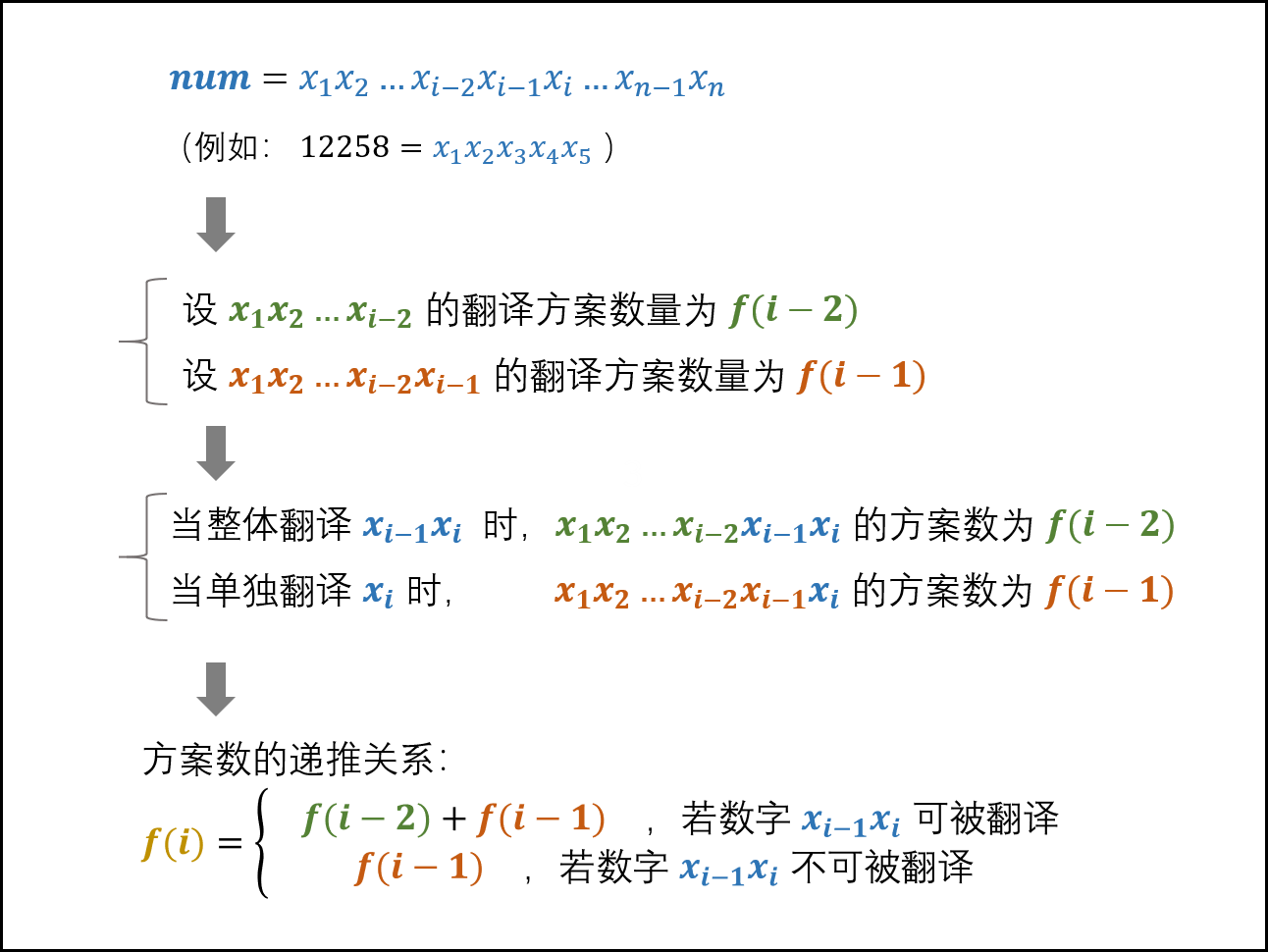
动态规划 记数字 num 第 i 位数字为 x~i~ ,数字 num 的位数为 n;
例如:num = 12283 的 n = 5,x~1~ = 1
状态定义:动态规划列表 dp,dp[i] 代表以 x~i~ 结尾的数字的翻译方案数量 转移方程:若 x~i~ 和 x~i-1~ 组成的两位数字可以被翻译(≥ 10 且 ≤ 25),则 dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2],否则 dp[i] = dp[i - 1]; 初始状态:dp[0] = dp[1] = 1 返回值:dp[n],即此数字的翻译方案数量 解题代码 由于 dp[i] 仅仅和 dp[i -1] 有关,所以可以用两个变量来替代他们进行迭代即可;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class Solution {public int translateNum (int num) {String str = String.valueOf(num);int p = 1 , q = 1 ;for (int i = 2 ; i <=str.length(); ++i) {String tmp = str.substring(i - 2 , i);int sum; if (tmp.compareTo("10" ) >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25" ) <= 0 ) {else {return p;
优化-求余 利用求余运算进一步减少 字符串 str 占用的空间复杂度 O(N) -> O(1)
public static int translateNum (int num) {int p = 1 , q = 1 , x, y = num % 10 ; while (num != 0 ) {10 ;10 ;int tmp = x * 10 + y;int sum = tmp >= 10 && tmp <= 25 ? p + q : p;return p;
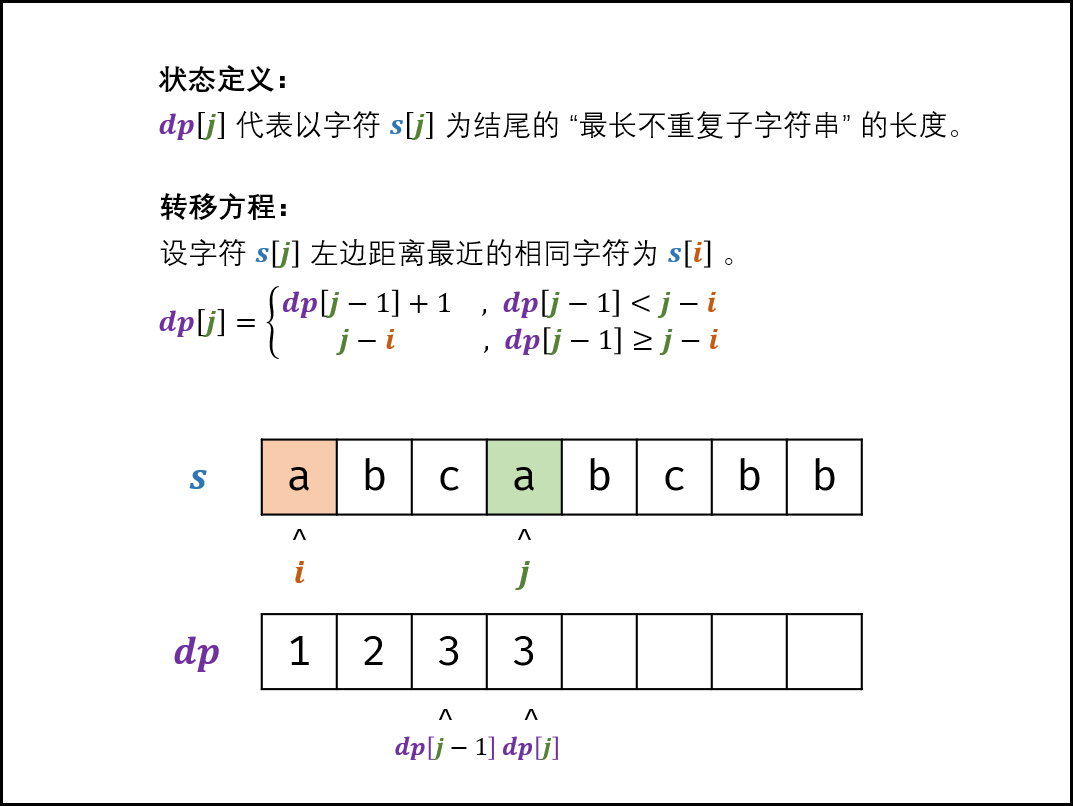
48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串 题目:剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
解题思路
状态定义: 设动态规划列表 dp,dp[j] 代表以字符 s[j] 为结尾的 “最长不重复子字符串” 的长度。
转移方程: 固定右边界 j ,设字符 s[j] 左边距离最近的相同字符为 s[i],即 s[i] = s[j]。
当 i < 0,即 s[j] 左边无相同字符,则 dp[j] = dp[j-1] + 1;
当 dp[j - 1] < j - i,说明字符 s[i] 在子字符串 dp[j−1] 区间之外,则 dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
当 dp[j−1] ≥ j − i,说明字符 s[i] 在子字符串 dp[j−1] 区间之中 ,则 dp[j] 的左边界由 s[i] 决定,即 dp[j] = j - i;
当 i < 0i<0 时,由于 dp[j - 1] \leq jdp[j−1]≤j 恒成立,因而 dp[j - 1] < j - idp[j−1]<j−i 恒成立,因此分支 1. 和 2. 可被合并
返回值: max(dp) ,即全局的 “最长不重复子字符串” 的长度。
解题代码
哈希表统计: 遍历字符串 s 时,使用哈希表统计 各个字符最后一次出现的索引 左边界 i 获取方式: 遍历到 s[i] 时,可通过访问哈希表获取到最近的相同字符串的索引 j;public class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {int max = 0 , tmp = 0 ;new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i) {int j = dic.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), -1 ); 1 : i - j; return max;
✔️Day 11 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十一天》
18. 删除链表的节点 题目:剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
解题思路
题目要求返回头节点,所以原先的头节点不能动;借助双指针完成更替操作,注意有个坑是需要删除的节点可能是头节点,此时需要改变头节点 head 的指向!
解题代码(双指针)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution {public ListNode deleteNode (ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null ) {return null ;ListNode cur = null , pre = head;while (pre != null ) {if (pre.val == val) {if (cur == null ) { else {break ;return head;
解题代码(单指针)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public ListNode deleteNode (ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null ) { return null ;if (head.val == val) { return head.next;ListNode pre = head;while (pre.next != null ) {if (pre.next.val == val) {break ;return head;
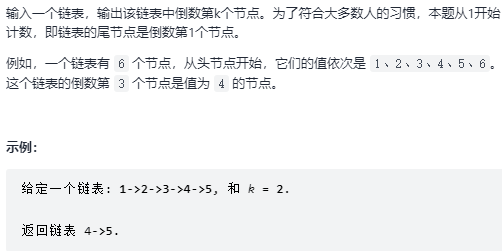
22. 链表中倒数第k个节点 题目:剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
解题代码
压栈后弹出 k - 1 个节点即可;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public ListNode getKthFromEnd (ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null ) {return null ;new Stack <>();while (head != null ) {while ((--k) > 0 ) {return stack.pop();
也可以借助 Java Stack 对象的方法 get
class Solution {public ListNode getKthFromEnd (ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null ) {return null ;new Stack <>();while (head != null ) {return stack.get(stack.size() - k);
题解思路 可以考虑先遍历统计链表长度,记为 n ;设置一个指针走 (n-k) 步,即可找到链表倒数第 k 个节点。
使用双指针,前指针 pre 先走 k 步,然后 前后指针 cur、pre 一起走,当 pre == null 时,返回 cur 即可;
public class Solution2 {public ListNode getKthFromEnd (ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || k == 0 ) {return null ;ListNode pre = head, cur = head;while ((k--) > 0 ) {while (pre != null ) {return cur;
✔️Day 12 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十二天》
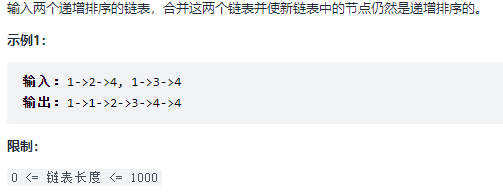
25. 合并两个排序的链表 题目:剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
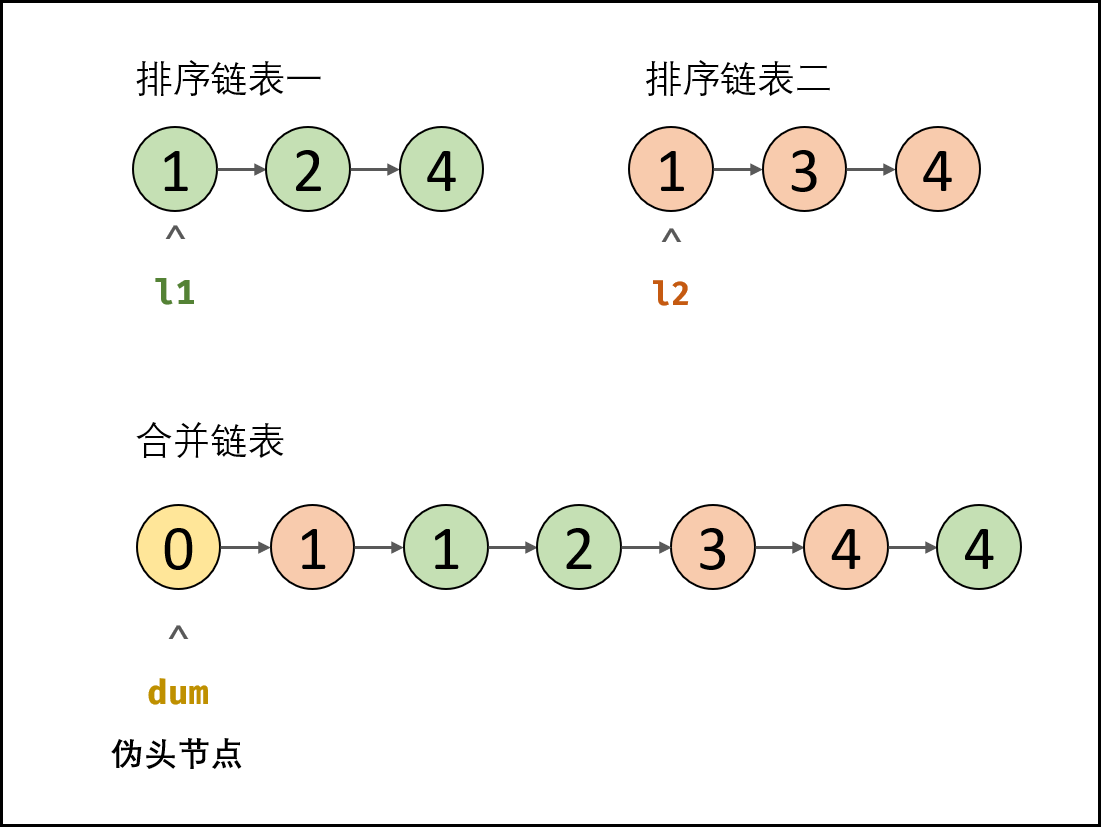
题解思路 自己想了半天,写了个错的!伤心,看了题解跟个人思路差不多,只能说大佬的图解太清晰了!链表的题目一定要自己画图,很容易出错!
引入伪头节点:由于初始状态合并链表中无节点,因此循环第一轮时无法将节点添加到合并链表中。解决方案:初始化一个辅助节点 dum 作为合并链表的伪头节点,将各节点添加至 dum 之后。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {if (l1 == null ) {return l2;if (l2 == null ) {return l1;ListNode head = new ListNode (0 );ListNode cur = head;while (l1 != null && l2 != null ) { if (l1.val < l2.val) {else {null ? l1 : l2; return head.next;
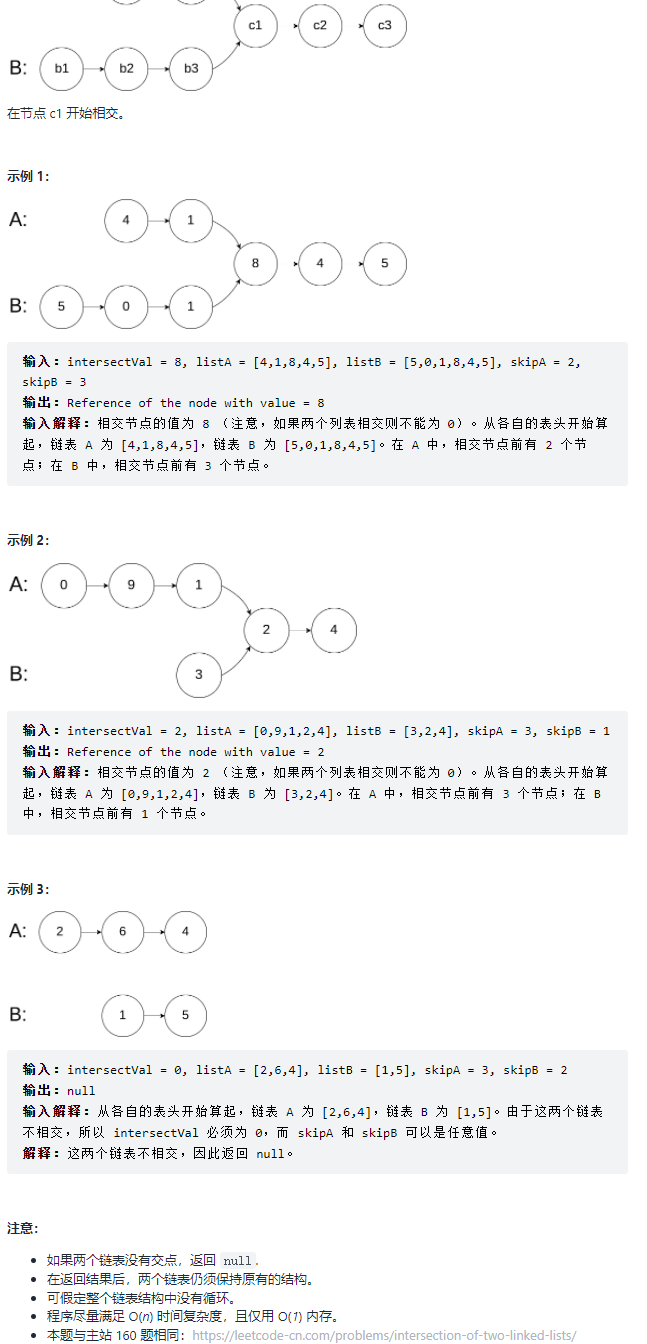
52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点 题目:剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
解题思路
这题之前在 CS-Notes 这里刷过了,很巧妙的思路,通过拼接两个链表 l1、l2,让两个链表达到长度相同的情况(l1 + l2 = l2 + l1)从而继续遍历;
设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问链表 A 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部重新开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问链表 B 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部重新开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null ) { return null ;ListNode l1 = headA, l2 = headB;while (l1 != l2) { null ? headB : l1.next;null ? headA : l2.next;return l1;
✔️Day 13 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十三天》
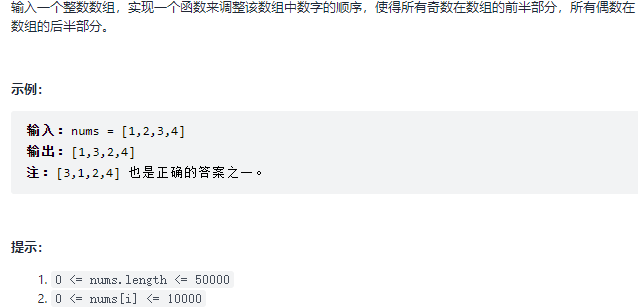
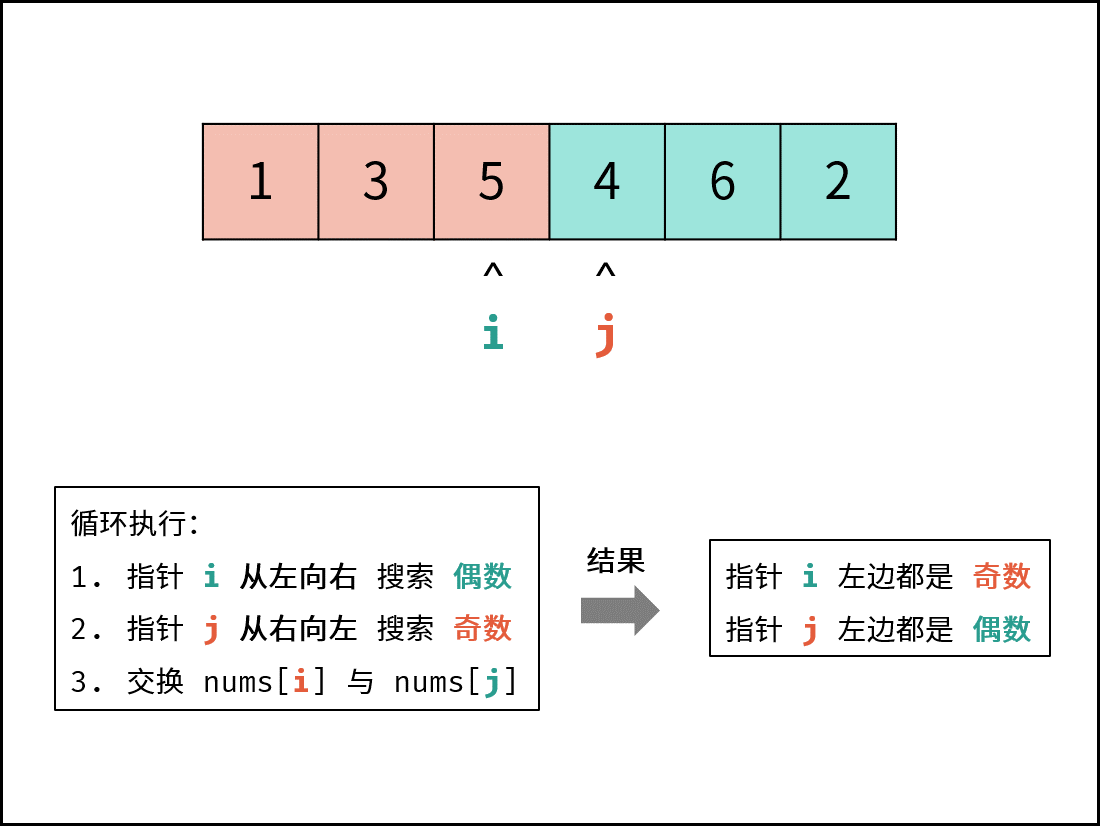
21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 题目:剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
解题思路
使用双指针遍历即可,指针 p 从头开始,指针 q 从末尾开始;执行下面的条件:
nums[p] 是偶数;p++ nums[q] 是奇数;q-- nums[p] 是偶数且nums[q] 是奇数,交换 nums[p] 和 nums[q] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution {public int [] exchange(int [] nums) {if (nums.length <= 1 ) {return nums;int p = 0 , q = nums.length - 1 ;while (p < q) {if ((nums[p] & 1 ) == 0 && (nums[q] & 1 ) == 1 ) { else if ((nums[p] & 1 ) == 1 && (nums[q] & 1 ) == 0 ){ else if ((nums[p] & 1 ) == 1 && (nums[q] & 1 ) == 1 ) { else { return nums;
题解思路 难得跟题解思路差不多了一次,题解对代码优化了很多,使得代码更简洁了;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Solution2 {public static void main (String[] args) {int [] ints = exchange(new int []{2 ,4 ,6 });for (int i : ints) {public static int [] exchange(int [] nums) {if (nums.length <= 1 ) {return nums;int p = 0 , q = nums.length - 1 , tmp;while (p < q) {while (p < q && (nums[p] & 1 ) == 1 ) { while (p < q && (nums[q] & 1 ) == 0 ) { return nums;
57. 和为s的两个数字 题目:剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
解题思路
简单题写多了,看到第一时间就想暴力出奇迹了,时间复杂度 O(n^2^)
利用双指针可以解题,一个在左端,一个在右端,相遇则返回;
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution {public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) {int p = 0 , q = nums.length - 1 ;while (p != q) {while (nums[p] + nums[q] < target) {while (nums[p] + nums[q] > target) {if (nums[p] + nums[q] == target) {return new int []{nums[p], nums[q]};return new int []{};
写完发现可以进行一点点的优化,nums[p] + nums[q] 多次计算了,可以 new 一个 Integer 类型对象去存储它,空间换时间;
public class Solution {public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) {int p = 0 , q = nums.length - 1 , sum;while (p < q) {if (sum < target) {else if (sum > target) {else {return new int []{nums[p], nums[q]};return new int []{};
因为此题是排序数组,所以可以进行这样的双指针操作,若不是排序数组,这样操作可能会导致丢失部分解;
日常借用 LeecCode K神 的图解:
题解思路 也看到了利用二分法求解的,利用哈希表求解的,题解多种多样,再尝试一下哈希表求解的:
public class Solution2 {public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) {new HashMap <>();for (int num : nums) {for (int num : nums) {int tmp = map.g etOrDefault (target - num, -1 ) ;if (tmp != -1 ) {return new int []{tmp, num};return new int []{};
时间复杂度挺高的:O(n^2^) 了,还不如直接遍历,还省内存,我是傻子哈哈~~~
58 - I. 翻转单词顺序 题目:剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution {public String reverseWords (String s) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();int p = s.length() - 1 , q = p;while (p >= 0 ) {while (p >= 0 && s.charAt(p) != ' ' ) {1 , q + 1 ).append(" " );while (p >= 0 && s.charAt(p) == ' ' ) {return builder.toString().trim();
题解思路 看了另一种方法是字符串分割,trim() 去除字符串首尾的空格并且返回修改后的字符串,split(" ") 是按照给定的字符串进行分割,可以使用正则表达式,” (两个空格)” 将会被分割为:["两个","","空格" ]
public static String reverseWords (String s) {" " );StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();for (int i = strings.length; i > 0 ; --i) {if (!"" .equals(strings[i - 1 ])) {1 ]).append(" " );return builder.toString().trim();
✔️Day 14 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十四天》
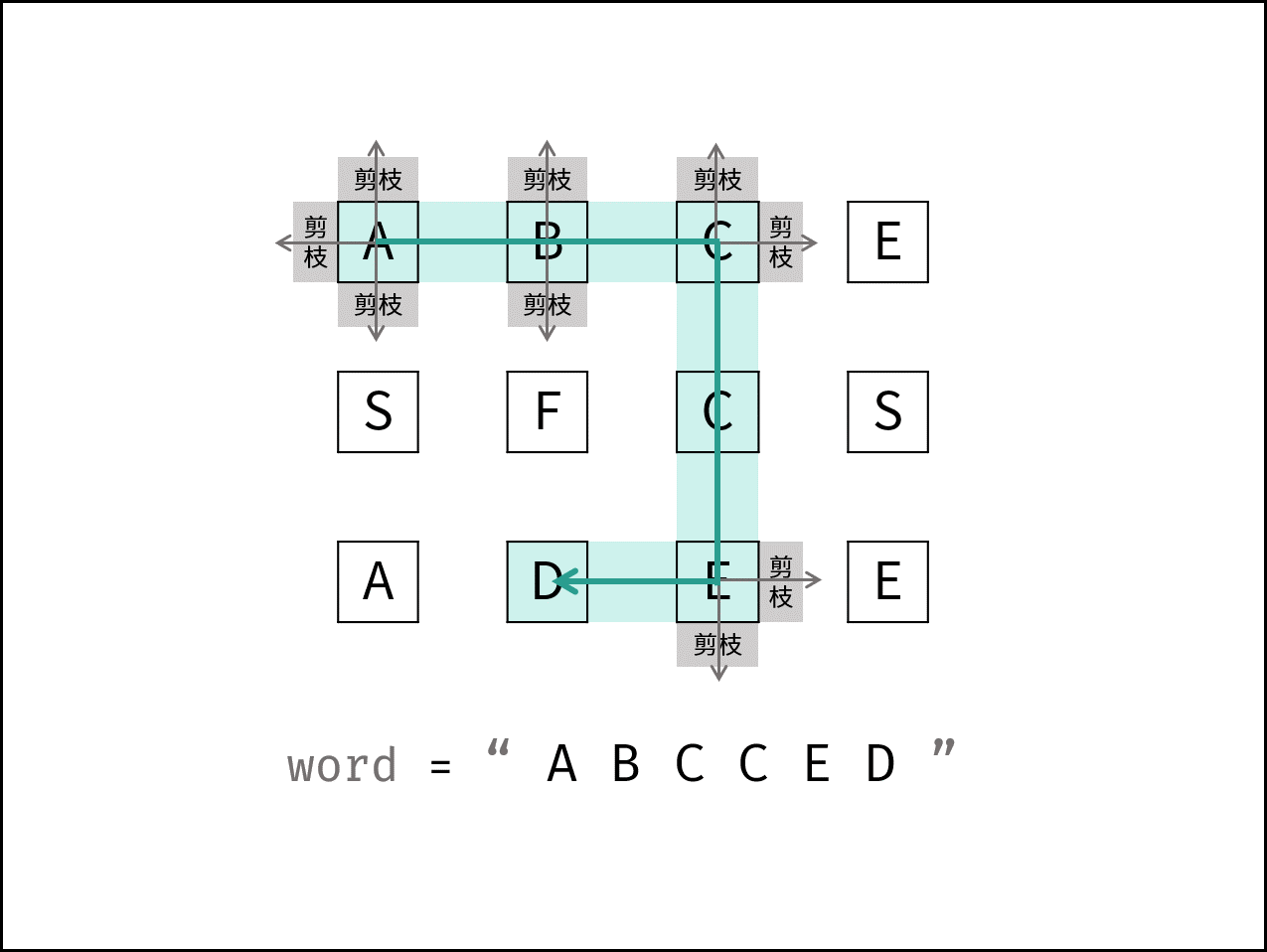
12. 矩阵中的路径 题目:剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
题解思路 本问题是典型的矩阵搜索问题,可使用 深度优先搜索(DFS)+ 剪枝 解决。
深度优先搜索: 可以理解为暴力法遍历矩阵中所有字符串可能性。DFS 通过递归,先朝一个方向搜到底,再回溯至上个节点,沿另一个方向搜索,以此类推。剪枝: 在搜索中,遇到 这条路不可能和目标字符串匹配成功 的情况(例如:此矩阵元素和目标字符不同、此元素已被访问 ),则应立即返回,称之为 可行性剪枝 。
DFS 解析:
递归参数: 当前元素在矩阵 board 中的行列索引 i 和 j ,当前目标字符在 word 中的索引 k ;终止条件: 返回 false :(1)行或列越界 或 (2)当前矩阵元素与目标字符不同 或 (3)当前矩阵元素已经访问过了((3)可以合并至(2)); 返回 true :k == words.length() - 1,即字符串 word 已全部匹配; 地推工作: 标记当前矩阵元素:将 board[i][j] 修改为 空字符 ‘\0’ ,代表此元素已经访问过,防止后续搜索时重复访问; 搜索下一单元格:朝当前元素的 上、下、左、右 四个方向开启下层递归,使用 || 连接(代表只需要找到一条可行路径就直接返回,不再做后续 DFS),并记录结果至 res; 还原当前矩阵元素:将 board[i][j] 元素还原至初始值,即 word[k]; 返回值: 返回布尔值 res,代表是否索搜到目标字符串;题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution {public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) {char [] words = word.toCharArray();for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < board[0 ].length; ++j) {if (dfs(board, words, i, j, 0 )) {return true ;return false ;public boolean dfs (char [][] board, char [] words, int i, int j, int k) {if (i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0 ].length || j < 0 || board[i][j] != words[k]) {return false ;if (k == words.length - 1 ) {return true ;'\0' ; boolean res = dfs(board, words, i + 1 , j, k + 1 ) || dfs(board, words, i - 1 , j, k + 1 ) ||1 , k + 1 ) || dfs(board, words, i, j - 1 , k + 1 );return res;
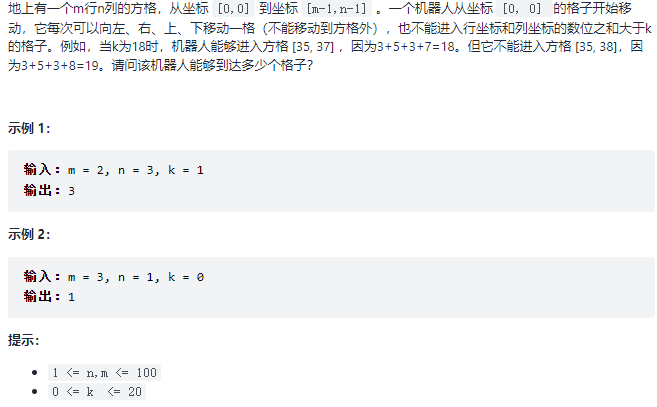
13. 机器人的运动范围 题目:剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
解题思路(dfs)
根据题解写了个最基本的 dfs,dfs 也被称作为 暴力算法,本质上就是枚举,可以解决没有办法确定枚举层数的问题;枚举 + 递归实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Solution {private int m, n, k;private boolean [][] visited;public int movingCount (int m, int n, int k) {this .m = m;this .n = n;this .k = k;this .visited = new boolean [m][n];return dfs(0 , 0 );public int dfs (int i, int j) {if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || visited[i][j]) { return 0 ;true ;if (sums(i) + sums(j) > k) { return 0 ;return 1 + (dfs(i + 1 , j) + dfs(i - 1 , j)1 ) + dfs(i, j - 1 ));public int sums (int num) {int tmp = 0 ;while (num != 0 ) {10 ;10 ;return tmp;
解题代码(dfs、优化)
然后看到评论区有大佬贴出来的代码,才发现这题的数据范围下标被限制到了 1<= n, m <= 100,也就是说索引值是在 0~99 之间的;所以可以省去 sums 这个函数的调用这一部分,然后又因为是从起点 (0, 0) 出发的,所以只需要向右下两个方向进行搜索即可;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution2 {private int m, n, k;private boolean [][] visited;public int movingCount (int m, int n, int k) {this .m = m;this .n = n;this .k = k;this .visited = new boolean [m][n];return dfs(0 , 0 );public int dfs (int i, int j) {if (i >= m || j >= n || visited[i][j]) { return 0 ;true ;if (i / 10 + i % 10 + j / 10 + j % 10 > k) { return 0 ;return 1 + dfs(i + 1 , j) + dfs(i, j + 1 );
题解思路(bfs) dfs 是深度优先搜索,一条路走到黑,bfs 是广度优先搜索,有种以 ”平推“ 的方式向前搜索;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public int movingCount (int m, int n, int k) {if (k == 0 ) {return 1 ;int []> queue = new LinkedList <>();boolean [][] visited = new boolean [m][n];0 ][0 ] = true ;int res = 1 ;new int []{0 , 0 });while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int [] cell = queue.poll(); int x = cell[0 ], y = cell[1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) {int tx = i + x;int ty = y + 1 - i;if (tx >= m || ty >= n || visited[tx][ty] || tx / 10 + tx % 10 + ty / 10 + ty % 10 > k) {continue ;new int []{tx, ty});true ;return res;
✔️Day 15 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十五天》
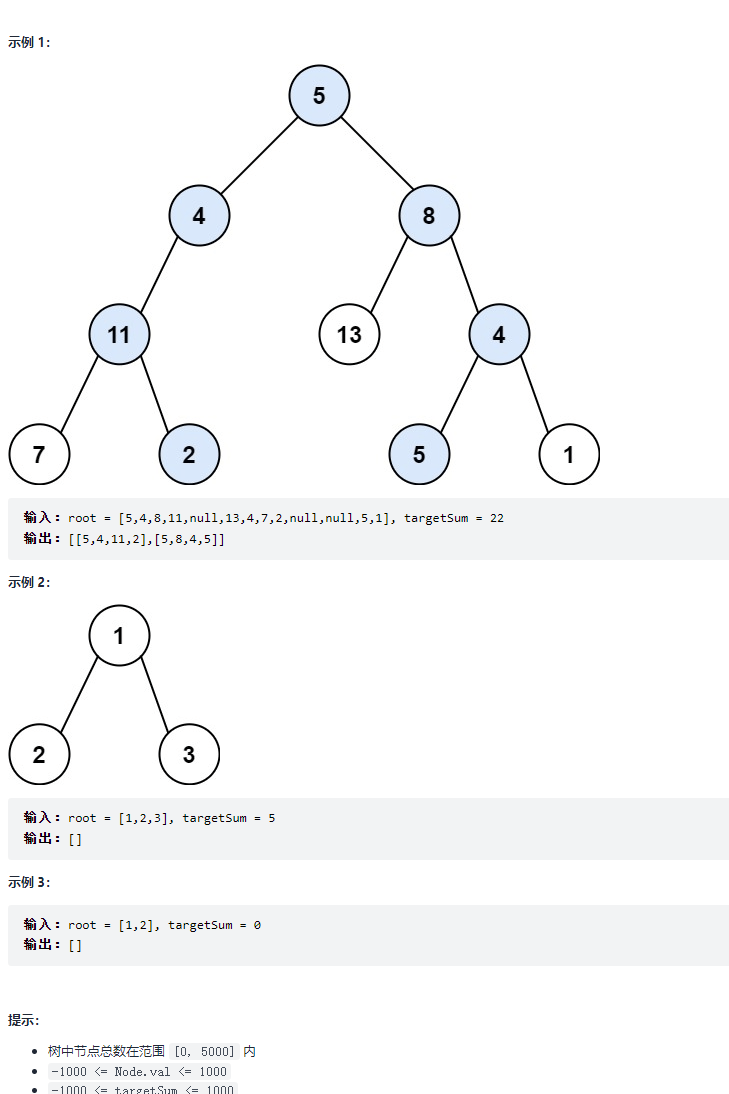
34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 题目:剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题解思路 本问题是典型的二叉树方案搜索问题,使用回溯法解决,其包含 先序遍历 + 路径记录 两部分
先序遍历: 按照 “根、左、右” 的顺序,遍历树的所有节点路径记录: 在先序遍历中,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径。当路径为:(1)根节点到叶节点形成的路径 且(2)各节点值的和等于目标值 sum 时,将此路径加入结果列表
算法流程
递推参数: 当前节点 root ,当前目标值 tar 。终止条件: 若节点 root 为空,则直接返回。递推工作: 路径更新: 将当前节点值 root.val 加入路径 path ; 目标值更新: tar = tar - root.val(即目标值 tar 从 sum 减至 0 ); 路径记录: 当 ① root 为叶节点 且 ② 路径和等于目标值 ,则将此路径 path 加入 res; 先序遍历: 递归左 / 右子节点; 路径恢复: 向上回溯前,需要将当前节点从路径 path 中删除,即执行 path.pop() ; 复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N): N 为二叉树的节点数,先序遍历需要遍历所有节点。 空间复杂度 O(N): 最差情况下,即树退化为链表时,path 存储所有树节点,使用 O(N) 额外空间。 题解代码
值得注意的是,记录路径时若直接执行 res.append(path) ,则是将 path 对象加入了 res ;后续 path 改变时, res 中的 path 对象也会随之改变
正确做法:res.append(list(path)) ,相当于复制了一个 path 并加入到 res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution {new LinkedList <>();new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int target) {return res;public void recur (TreeNode root, int target) {if (root == null ) {return ;if (target == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null ) { new LinkedList <>(path));
36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表 题目:剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树:中序遍历是递增序列的数
(一个节点的左子树的所有节点的值比它小,右子树的所有节点的值比它大)
解题思路
想到中序遍历了,然后第一时间想用栈去存储它,但是想不到怎么从一开始获取栈顶栈顶的元素(head、tail 节点),最后干脆使用 ArrayList 去存储它了;
借个 K 神的图:
解题代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Solution {private ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList <>();public Node treeToDoublyList (Node root) {if (root == null ) { return null ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { return root;Node head = list.get(0 ), tail = list.get(list.size() - 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size() - 1 ; ++i) {1 );1 ).left = list.get(i);return head;public void recur (Node root) { if (root == null ) {return ;if (root.left != null ) {if (root.right != null ) {
54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点 题目:剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
题解思路 二叉搜索树的的中序遍历是递增序列,需要找第 k 大的节点,如果是降序序列会容易一点;中序遍历的过程是:左 中 右,而先 右 中 左 就能满足降序序列,所以将遍历条件稍微修改一下就可以了;
题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution {private int res, k;public int kthLargest (TreeNode root, int k) {this .k = k;return res;public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return ;if (k == 0 ) {return ;if (k == 0 ) {
✔️Day 16 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十六天》
45. 把数组排成最小的数 题目:剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
解题思路
首先确定一件事就是,不管怎么排序,最后得到的数字的位数都是一样的(特例:前导 0,所以要进行特判)所以每次从数组中找到,高位最小值即可(相同值比较次高位)
例如:
写了两个小时,我承认我是废物了,呜呜,好的看题解去了,写不出来;垃圾代码就不贴出来了
题解思路 大佬不愧是大佬,思路清晰欸,人家直接追根溯源,假设两个数 x 和 y,若拼接后的数字 x + y > y + x,则 x 在本题逻辑上大于 y;
题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution {public String minNumber (int [] nums) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();int tmp;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < nums.length - 1 - i; ++j) {if (compare(nums[j], nums[j + 1 ]) > 0 ) {1 ];1 ] = tmp;for (int num : nums) {return builder.toString();public int compare (int num1, int num2) {return ("" + num1 + num2)"" + num2 + num1);
题解代码(优化)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution {public String minNumber (int [] nums) { new String [nums.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++)0 , strs.length - 1 );StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder ();for (String s : strs)return res.toString();void quickSort (String[] strs, int l, int r) {if (l >= r) return ;int i = l, j = r;String tmp = strs[i];while (i < j) {while ((strs[j] + strs[l]).compareTo(strs[l] + strs[j]) >= 0 && i < j) j--;while ((strs[i] + strs[l]).compareTo(strs[l] + strs[i]) <= 0 && i < j) i++;1 );1 , r);
61. 扑克牌中的顺子 题目:剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
解题思路
此题有个小坑,需要注意的是从若干副扑克牌中抽取五张牌,并不是一副扑克牌中,所以有可能会出现如下的特例:[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
俺没有很好的抽象思维能力,根据样例想出来了若没有癞子将数组通过两两迭代(无需排序)最后结果为 4 就可以(等差数列),然后就成功写出来了垃圾代码,居然还通过了 95% 的样例;
之后考虑上癞子卡了一会,提交失败后发现特例:[0, 0, 2, 2, 5];于是发现了自己没有进行相同非癞子牌的判别,加入特判后成功通过;
解题代码
public boolean isStraight (int [] nums) {int joker = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) {if (nums[i] == 0 ) {else if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1 ]){return false ;return nums[4 ] - nums[joker] < 5 ;
题解思路
看了下题解,难得自己和大佬代码写了一样了一次,然后还有一种思路是通过 set 去维护牌组,若有相同的直接返回 false,其他操作一样;
public boolean isStraight (int [] nums) {new HashSet <>();int max = 0 , min = 14 ;for (int num: nums) {if (num == 0 ) continue ;if (set.contains(num)) {return false ;return max - min < 5 ;
✔️Day 17 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十七天》
40. 最小的k个数 题目:剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数
解题思路
第一时间想到了冒泡排序,找出 k 大的有序区域返回即可;提交通过后那个用时和内存消耗把自己整笑了,又是写了垃圾代码的一天;
解题代码
public class Solution {public int [] getLeastNumbers(int [] arr, int k) {int tmp;for (int i = 0 ; i < k; ++i) {for (int j = arr.length - 1 ; j > i; --j) {if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1 ]) {1 ];1 ] = tmp;return Arrays.copyOf(arr, k);
41. 数据流中的中位数 题目:剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数
思路
第一时间想到的是维护一个有序的动态数组,然后用个“指针”一直指向中间元素,根据数组元素的奇、偶去获取中值,但是想了想这么做好像没法剑指offer了,面试官可能一脚给我踢出来了,所以看了题解去了;
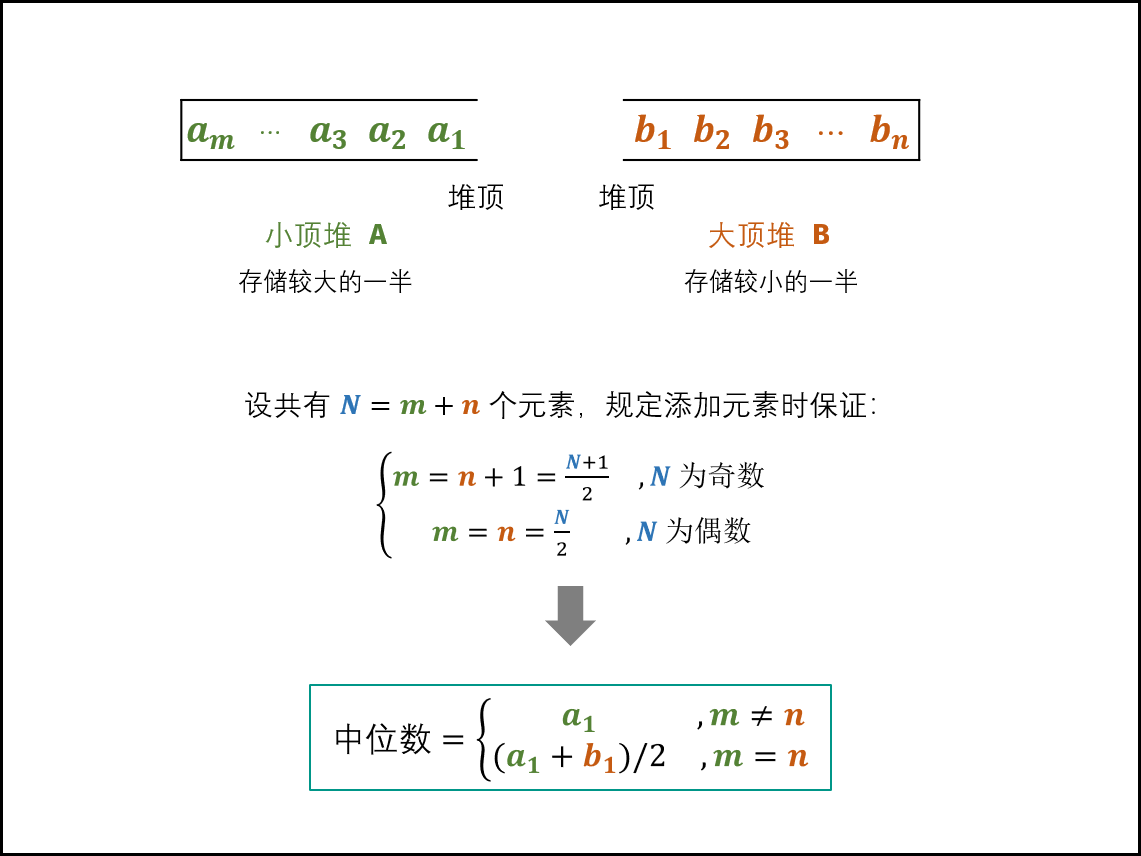
题解思路 借助 堆 进一步优化时间复杂度,建立一个小顶堆 A 和 大顶堆 B,各保存列表的一半元素,且规定:
A 保存 较大 的一半,长度为 $\frac{N}{2}$( N 为偶数)或 $\frac{N + 1}{2}$ (N 为奇数) B 保存 较小 的一半,长度为 $\frac{N}{2}$ (N 为偶数)或 $\frac{N - 1}{2}$ (N 为奇数)
算法流程
设元素总数为 N = m + n,其中 m 和 n 分别为 A 和 B 中的元素个数。
A 小顶堆中存储较大的一半,B 大顶堆中存储较小的一半,这样之后 A 的堆顶的值 >= B的堆顶的值,即 A 中的最小值大于等于 B 中的最大值;
addNum(num) 函数:
当 m = n(即 N 为偶数):需向 A 添加一个元素,实现方法:将新元素 num 插入 B,再将 B 堆顶元素插入至 A(确保上面的那个性质) 当 m != n(即 N 为奇数):需向 B 添加一个元素。实现方法:将新元素 num 插入至 A ,再将 A 堆顶元素插入至 B ; findMedian() 函数:
当 m = n (N 为偶数):则中位数为(A 的堆顶元素 + B 的堆顶元素)/ 2 当 m != n (N 为奇数):则中位数为 A 的堆顶元素; 复杂度分析
时间复杂度:查找中位数 O(1):获取堆顶元素使用 O(1) 时间 添加数字 O(log N):堆的插入和弹出操作使用 O(log N) 时间 空间复杂度 O(N):其中 N 为数据流中的元素数量,小顶堆 A 和大顶堆 B 最多同时保存 N 个元素 题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class MedianFinder {public static void main (String[] args) {new PriorityQueue <>();new PriorityQueue <>((x, y) -> y - x);new PriorityQueue <>(new Comparator <Integer>() {@Override public int compare (Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2 - o1;private Queue<Integer> A, B;public MedianFinder () {new PriorityQueue <>();new PriorityQueue <>((x, y) -> (y - x));public void addNum (int num) {if (A.size() != B.size()) {else {public double findMedian () {return A.size() != B.size() ? A.peek() : (A.peek() + B.peek()) / 2.0 ;
✔️Day 18 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十八天》
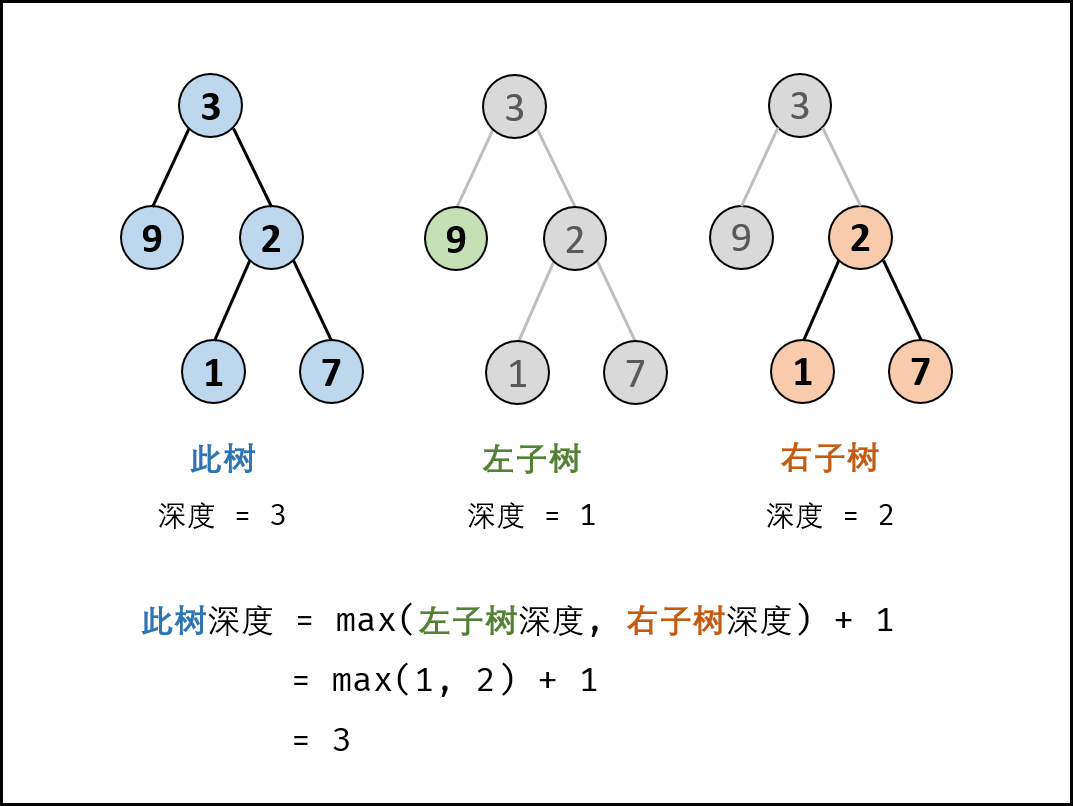
55 - I. 二叉树的深度 题目:剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
稍微分析之后可以得出规律:对于一个非叶子节点的节点 node,它的深度为 max(deep(node.left), deep(node.right)) + 1,所以可以很轻松写出来递归解法:
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N):N 为树的节点个数,dfs 计算需要遍历到树的每一个节点; 空间复杂度 O(N):最差情况下(树退化为链表时(所有非叶子节点都只有一个方向上的子节点)),递归深度可达到 N 解题代码
public class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1 ;
题解思路 二叉树的常见四种遍历方式中,层序遍历(BFS)显然与深度有关,可以在层序遍历的过程中每遍历一层使用计数器统计深度即可;
题解代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;new LinkedList <>();int res = 0 ;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0 ;--i) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null ) queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right);return res;
55 - II. 平衡二叉树 题目:剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
解题思路
在上一题的基础上对每个非叶子节点进行判断即可;有许多重复性的操作,效率较低;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return true ;return (Math.abs(dfs(root.left) - dfs(root.right)) <= 1 )public int dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int left = dfs(root.left);int right = dfs(root.right);return Math.max(left, right) + 1 ;
题解思路 在原有基础上进行剪枝,当发现已经不是 平衡二叉树 时,提前返回;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {return dfs(root) != -1 ;public int dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int left = dfs(root.left);if (left == -1 ) {return -1 ;int right = dfs(root.right);if (right == -1 ) {return -1 ;return Math.abs(left - right) < 2 ? Math.max(left, right) + 1 : -1 ;
✔️Day 19 刷题笔记:《剑指 Offer 第十九天》
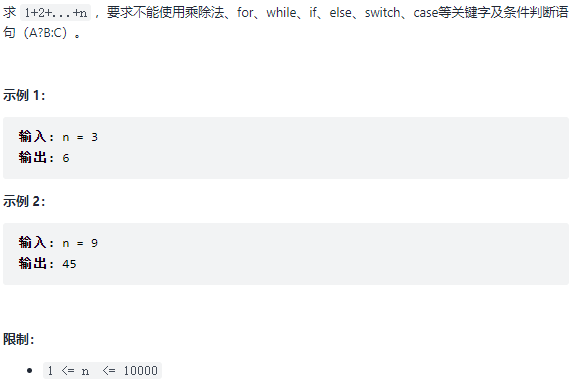
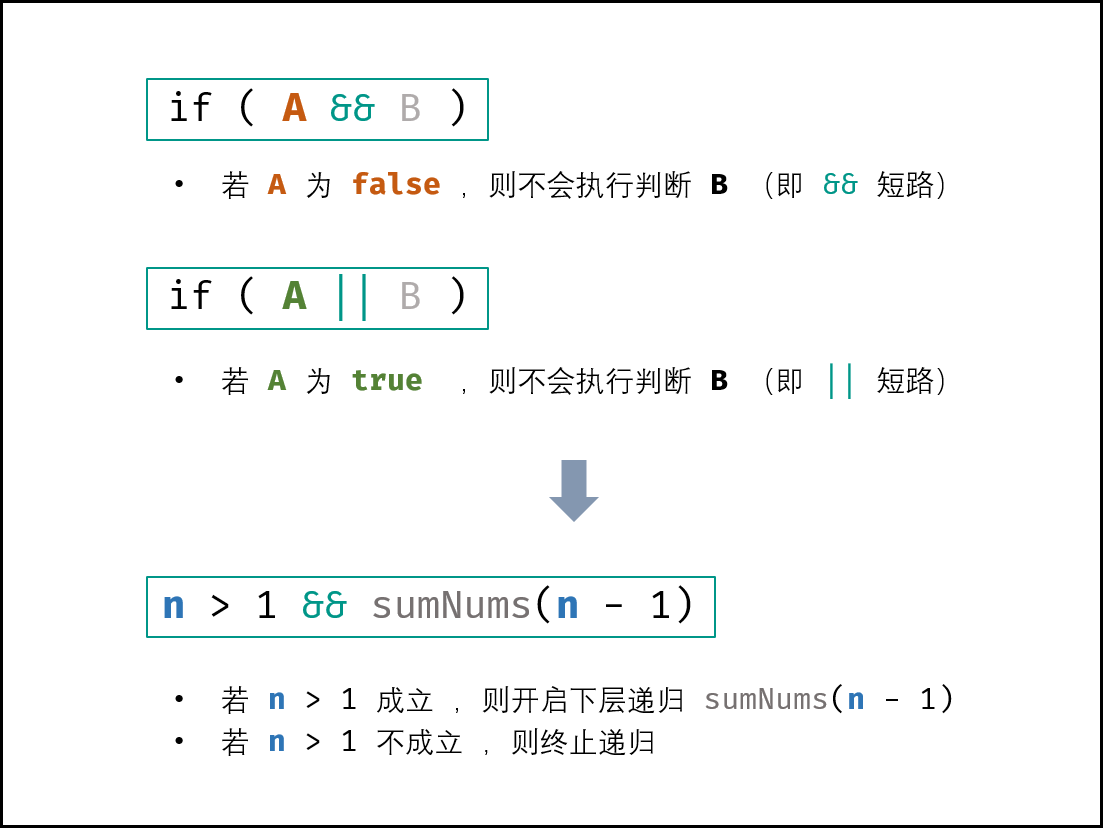
64. 求1+2+…+n 题目:剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
题解思路 我想打表,他说我代码太长了,哭,他把我能用的符号都给 ban 了,我实在是想不到思路了,看了评论区,秀的我天花乱坠;
有面试官看到了就请你出去类型的题解:
int sumNums (int n) { return int (Math.pow(n, 2 ) + n) >> 1 ;
也有我不知道怎么翻译到 Java 类型的 C++ 题解:
int sumNums (int n) bool arr[n][n+1 ];return sizeof (arr) >> 1 ;
有C语言内联汇编的(汇编都出来了,牛的)题解:
int sumNums (int n) { int res;"movl %%edi, %%eax\n" "incl %%edi\n" "imull %%edi\n" "shrl $1, %%eax\n" "=a" (res)return res;
还有自己实现乘法逻辑的题解:
int sumNums (int n) { return multiply(n,n+1 ) >> 1 ; int multiply (int A, int B) {int res = B;1 ) && (res = ((( -(A & 1 )) & B) + multiply(A >> 1 , B << 1 ))); return res;
还有我想到了递归却想不到究竟该如何求解类型的题解:
int sumNums (int n) { int sum = n;boolean flag = n > 0 && sum += sumNums(n - 1 ) > 0 ;return sum;
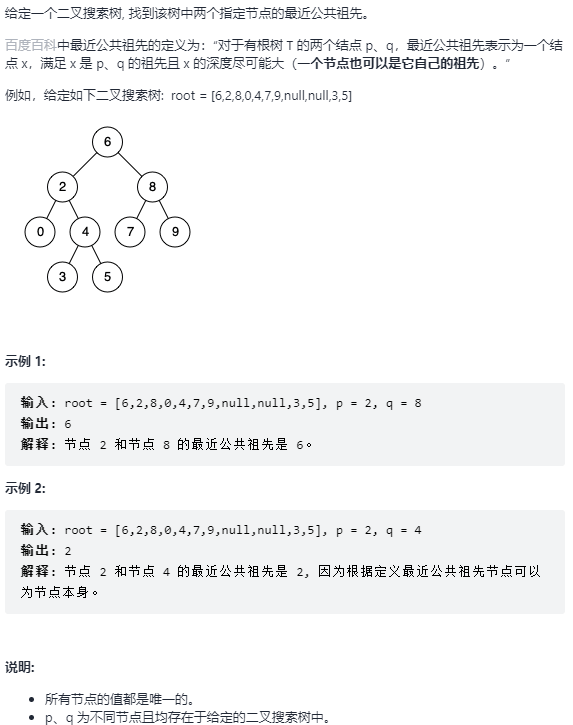
68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 题目:剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
解题思路
二叉搜索树 有如下的性质: 对于一个非叶子节点,它的左节点的值比它小,它的右节点的值比它大。
给定的条件还有所有的节点值都是 唯一且存在的 ,所以可以根据节点 p、q 的值去判断节点 p、q 和 根节点 root 的位置关系;
p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val:p、q 在 root 节点的左子树上,遍历 root.left ;p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val:p、q 在 root 节点的右子树上,遍历 root.right ;p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val:p(或 q) 是 q(或 p) 的父节点,直接返回 root 即可;p.val < root.val && q.val > root.val || p.val > root.val && q.val < root.val:p、q 在 root 节点的两侧,直接返回 root 即可;解题代码
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val > root.val && q.val < root.val || p.val < root.val && q.val > root.val || p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val) {return root;if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
解题代码—优化?
emmmmm,优化完提交了一下才发现好像是负面优化:5ms 42.5MB -> 6ms 42.4MB,但是代码逻辑上来说更清晰了,负面优化的原因应该是: 递归终止条件没在开头
public class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) { return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) { return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);return root;
解题代码—再优化
如果可以保证 p、q 的大小一定(例如:p < q),那么可以省去许多判断;5ms 42.5MB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val > q.val) {TreeNode tmp = p;return recur(root, p, q);public TreeNode recur (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (q.val < root.val) { return recur(root.left, p, q);if (p.val > root.val) { return recur(root.right, p, q);return root;
5ms 42.4 MB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution {public static TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val > q.val) {TreeNode tmp = p;return recur(root, p, q);public static TreeNode recur (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val < root.val && q.val > root.val || p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val) {return root;if (q.val < root.val) {return recur(root.left, p, q);return recur(root.right, p, q);
题解代码(非递归) 5ms 42.2 MB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p.val > q.val) { TreeNode tmp = p;while (root != null ) {if (root.val < p.val) else if (root.val > q.val) else break ;return root;
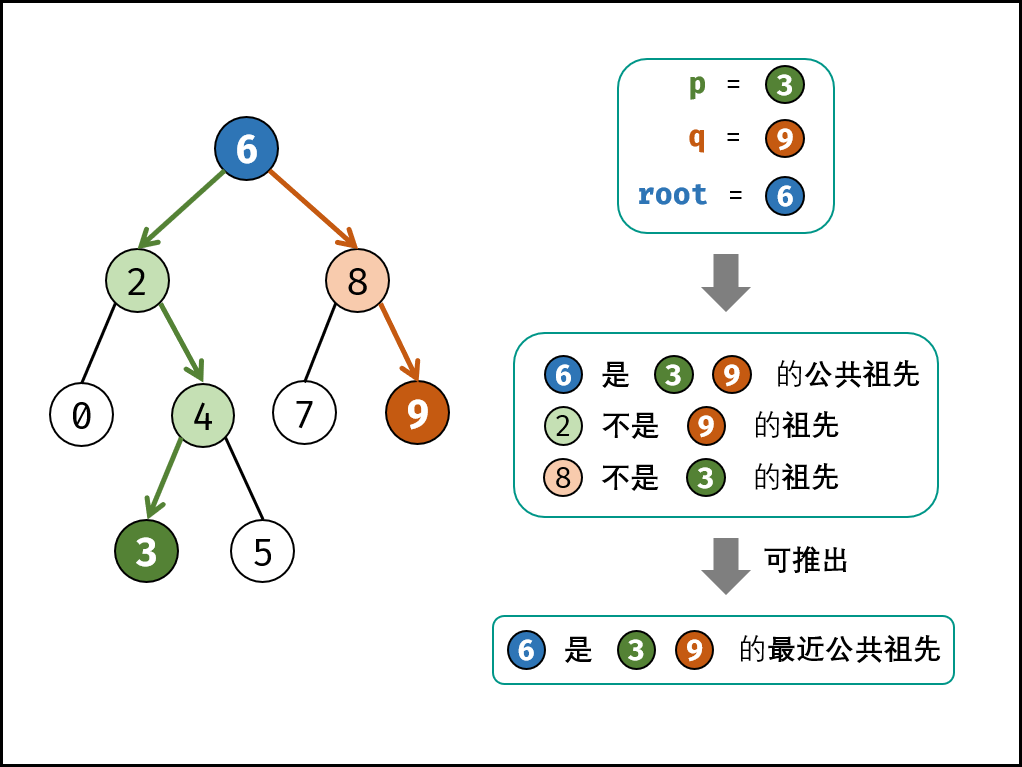
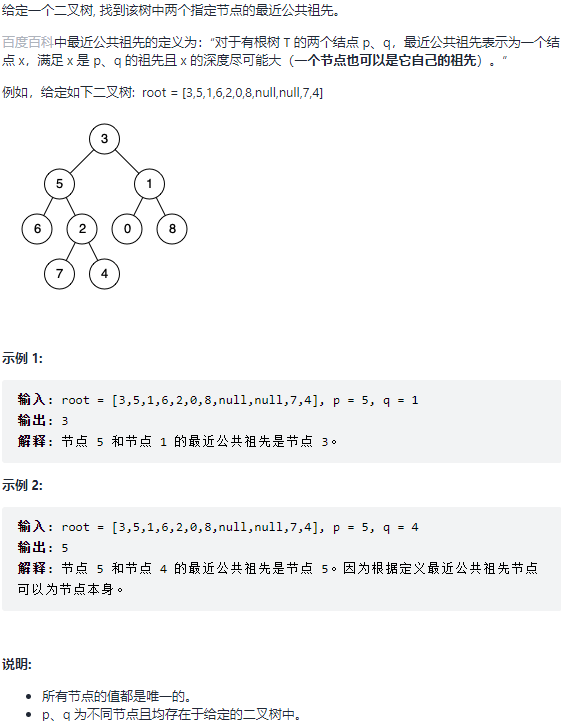
68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 题目:剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
解题思路 与上一题不同的是这是一颗普通的二叉树,也就是没有了: 对于一个非叶子节点,它的左节点的值比它小,它的右节点的值比它大。 这个性质了;